Cytotoxic necrotizing factor-Y boosts Yersinia effector translocation by activating Rac protein
- PMID: 23803609
- PMCID: PMC3949328
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.448662
Cytotoxic necrotizing factor-Y boosts Yersinia effector translocation by activating Rac protein
Abstract
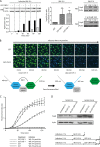
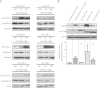
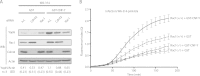
Pathogenic Yersinia spp. translocate the effectors YopT, YopE, and YopO/YpkA into target cells to inactivate Rho family GTP-binding proteins and block immune responses. Some Yersinia spp. also secrete the Rho protein activator cytotoxic necrotizing factor-Y (CNF-Y), but it has been unclear how the bacteria may benefit from Rho protein activation. We show here that CNF-Y increases Yop translocation in Yersinia enterocolitica-infected cells up to 5-fold. CNF-Y strongly activated RhoA and also delayed in time Rac1 and Cdc42, but when individually expressed, constitutively active mutants of Rac1, but not of RhoA, increased Yop translocation. Consistently, knock-out or knockdown of Rac1 but not of RhoA, -B, or -C inhibited Yersinia effector translocation in CNF-Y-treated and control cells. Activation or knockdown of Cdc42 also affected Yop translocation but much less efficiently than Rac. The increase in Yop translocation induced by CNF-Y was essentially independent of the presence of YopE, YopT, or YopO in the infecting Yersinia strain, indicating that none of the Yops reported to inhibit translocation could reverse the CNF-Y effect. In summary, the CNF-Y activity of Yersinia strongly enhances Yop translocation through activation of Rac.
Keywords: CNF-Y; Cdc42; Cytotoxic Necrotizing Factor-Y; Rac; Rho; Rho GTPases; Toxins; Type III Secretion System; Yersinia enterocolitica.
Figures

References
-
- Prentice M. B., Rahalison L. (2007) Plague. Lancet 369, 1196–1207 - PubMed
-
- Viboud G. I., Bliska J. B. (2005) Yersinia outer proteins: role in modulation of host cell signaling responses and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 59, 69–89 - PubMed
-
- Trülzsch K., Oellerich M. F., Heesemann J. (2007) Invasion and dissemination of Yersinia enterocolitica in the mouse infection model. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 603, 279–285 - PubMed
-
- Heesemann J., Sing A., Trülzsch K. (2006) Yersinia's stratagem: targeting innate and adaptive immune defense. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 9, 55–61 - PubMed
-
- Navarro L., Alto N. M., Dixon J. E. (2005) Functions of the Yersinia effector proteins in inhibiting host immune responses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 8, 21–27 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

