Surface-mediated bone tissue morphogenesis from tunable nanolayered implant coatings
- PMID: 23803705
- PMCID: PMC4001255
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005576
Surface-mediated bone tissue morphogenesis from tunable nanolayered implant coatings
Abstract
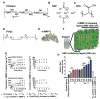
The functional success of a biomedical implant critically depends on its stable bonding with the host tissue. Aseptic implant loosening accounts for more than half of all joint replacement failures. Various materials, including metals and plastic, confer mechanical integrity to the device, but often these materials are not suitable for direct integration with the host tissue, which leads to implant loosening and patient morbidity. We describe a self-assembled, osteogenic, polymer-based conformal coating that promotes stable mechanical fixation of an implant in a surrogate rodent model. A single modular, polymer-based multilayered coating was deposited using a water-based layer-by-layer approach, by which each element was introduced on the surface in nanoscale layers. Osteoconductive hydroxyapatite (HAP) and osteoinductive bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) contained within the nanostructured coating acted synergistically to induce osteoblastic differentiation of endogenous progenitor cells within the bone marrow, without indications of a foreign body response. The tuned release of BMP-2, controlled by a hydrolytically degradable poly(β-amino ester), was essential for tissue regeneration, and in the presence of HAP, the modular coating encouraged the direct deposition of highly cohesive trabecular bone on the implant surface. In vivo, the bone-implant interfacial tensile strength was significantly higher than standard bioactive bone cement, did not fracture at the interface, and had long-term stability. Collectively, these results suggest that the multilayered coating system promotes biological fixation of orthopedic and dental implants to improve surgical outcomes by preventing loosening and premature failure.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

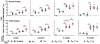




References
-
- Labek G, Thaler M, Janda W, Agreiter M, Stöckl B. Revision rates after total joint replacement: cumulative results from worldwide joint register datasets. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93:293–297. - PubMed
-
- Lewis G. Alternative acrylic bone cement formulations for cemented arthroplasties: Present status, key issues, and future prospects. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 2007;84:301–319. - PubMed
-
- Berger RA, Lyon JH, Jacobs JJ, Barden RM, Berkson EM, Sheinkop MB, Rosenberg AG, Galante JO. Problems with cementless total knee arthroplasty at 11 years followup. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;392:196–207. - PubMed
-
- Sun L, Berndt CC, Gross KA, Kucuk A. Material fundamentals and clinical performance of plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings: a review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2001;58:570–592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

