Estrogen mediates neuroprotection and anti-inflammatory effects during EAE through ERα signaling on astrocytes but not through ERβ signaling on astrocytes or neurons
- PMID: 23804112
- PMCID: PMC3693061
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0886-13.2013
Estrogen mediates neuroprotection and anti-inflammatory effects during EAE through ERα signaling on astrocytes but not through ERβ signaling on astrocytes or neurons
Abstract
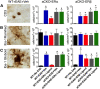
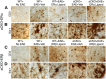
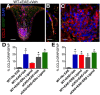
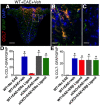
Estrogens can signal through either estrogen receptor α (ERα) or β (ERβ) to ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), the most widely used mouse model of multiple sclerosis (MS). Cellular targets of estrogen-mediated neuroprotection are still being elucidated. Previously, we demonstrated that ERα on astrocytes, but not neurons, was critical for ERα ligand-mediated neuroprotection in EAE, including decreased T-cell and macrophage inflammation and decreased axonal loss. Here, we determined whether ERβ on astrocytes or neurons could mediate neuroprotection in EAE, by selectively removing ERβ from either of these cell types using Cre-loxP gene deletion. Our results demonstrated that, even though ERβ ligand treatment was neuroprotective in EAE, this neuroprotection was not mediated through ERβ on either astrocytes or neurons and did not involve a reduction in levels of CNS inflammation. Given the differential neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects mediated via ERα versus ERβ on astrocytes, we looked for molecules within astrocytes that were affected by signaling through ERα, but not ERβ. We found that ERα ligand treatment, but not ERβ ligand treatment, decreased expression of the chemokines CCL2 and CCL7 by astrocytes in EAE. Together, our data show that neuroprotection in EAE mediated via ERβ signaling does not require ERβ on either astrocytes or neurons, whereas neuroprotection in EAE mediated via ERα signaling requires ERα on astrocytes and reduces astrocyte expression of proinflammatory chemokines. These findings reveal important cellular differences in the neuroprotective mechanisms of estrogen signaling through ERα and ERβ in EAE.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neuroprotection mediated through estrogen receptor-alpha in astrocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 24;108(21):8867-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103833108. Epub 2011 May 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21555578 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with an estrogen receptor alpha ligand is neuroprotective in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J Neurosci. 2006 Jun 21;26(25):6823-33. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0453-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16793889 Free PMC article.
-
Lentivirus-mediated estrogen receptor α overexpression in the central nervous system ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice.Int J Mol Med. 2013 May;31(5):1209-21. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1306. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Int J Mol Med. 2013. PMID: 23525227
-
Nudging oligodendrocyte intrinsic signaling to remyelinate and repair: Estrogen receptor ligand effects.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jun;160:43-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.01.006. Epub 2016 Jan 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26776441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen-mediated protection of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis: Lessons from the dissection of estrogen receptor-signaling in vivo.Biomed J. 2015 May-Jun;38(3):194-205. doi: 10.4103/2319-4170.158509. Biomed J. 2015. PMID: 26068028 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation and the Mechanism of Estrogen on Cav1.2 Gene in Rat-Cultured Cortical Astrocytes.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Oct;60(2):205-13. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0803-y. Epub 2016 Aug 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27498200
-
NogoA-expressing astrocytes limit peripheral macrophage infiltration after ischemic brain injury in primates.Nat Commun. 2021 Nov 25;12(1):6906. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27245-0. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34824275 Free PMC article.
-
The novel estrogenic receptor GPR30 alleviates ischemic injury by inhibiting TLR4-mediated microglial inflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Jul 12;15(1):206. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1246-x. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 30001721 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent regulation of obesity and Alzheimer-related outcomes by hormone therapy in female 3xTg-AD mice.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 2;12(6):e0178490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178490. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28575011 Free PMC article.
-
Estradiol improves right ventricular function in rats with severe angioproliferative pulmonary hypertension: effects of endogenous and exogenous sex hormones.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 May 1;308(9):L873-90. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00006.2015. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25713318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adzemovic MZ, Öckinger J, Zeitelhofer M, Hochmeister S, Beyeen AD, Paulson A, Gillett A, Thessen Hedreul M, Covacu R, Lassmann H, Olsson T, Jagodic M. Expression of Ccl11 associates with immune response modulation and protection against neuroinflammation in rats. PLoS One. 2012;7:e39794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039794. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argaw AT, Asp L, Zhang J, Navrazhina K, Pham T, Mariani JN, Mahase S, Dutta DJ, Seto J, Kramer EG, Ferrara N, Sofroniew MV, John GR. Astrocyte-derived VEGF-A drives blood–brain barrier disruption in CNS inflammatory disease. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:2454–2468. doi: 10.1172/JCI60842. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
