A rule-based kinetic model of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation
- PMID: 23804443
- PMCID: PMC3730697
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2013.0438
A rule-based kinetic model of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain phosphorylation
Abstract
The complexity of many RNA processing pathways is such that a conventional systems modelling approach is inadequate to represent all the molecular species involved. We demonstrate that rule-based modelling permits a detailed model of a complex RNA signalling pathway to be defined. Phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) C-terminal domain (CTD; a flexible tail-like extension of the largest subunit) couples pre-messenger RNA capping, splicing and 3' end maturation to transcriptional elongation and termination, and plays a central role in integrating these processes. The phosphorylation states of the serine residues of many heptapeptide repeats of the CTD alter along the coding region of genes as a function of distance from the promoter. From a mechanistic perspective, both the changes in phosphorylation and the location at which they take place on the genes are a function of the time spent by RNAPII in elongation as this interval provides the opportunity for the kinases and phosphatases to interact with the CTD. On this basis, we synthesize the available data to create a kinetic model of the action of the known kinases and phosphatases to resolve the phosphorylation pathways and their kinetics.
Keywords: Kappa; rule-based modelling; transcription.
Figures

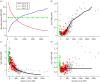
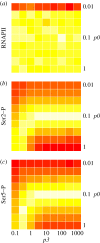

References
-
- Ollivier JF, Shahrezaei V, Swain PS. 2010. Scalable rule-based modelling of allosteric proteins and biochemical networks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 6, e1000975. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000975 (doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000975) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachman JA, Sorger P. 2011. New approaches to modeling complex biochemistry. Nat. Methods 8, 130–131 10.1038/nmeth0211-130 (doi:10.1038/nmeth0211-130) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Danos V, Feret J, Fontana W, Harmer R, Krivine J. 2007. Rule-based modelling of cellular signalling. In CONCUR 2007: concurrency theory (eds Caires L, Vasconcelos V.). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 4703, pp. 17–41 Berlin, Germany: Springer
-
- Elliot D, Ladomery M. 2011. Molecular biology of RNA. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press
-
- Palancade B, Marshall NF, Tremeau-Bravard A, Bensaude O, Dahmus ME, Dubois M-F. 2004. Dephosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by CTD-phosphatase FCP1 is inhibited by phospho-CTD associating proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 335, 415–424 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.036 (doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.10.036) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
