Proximal tubule PPARα attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation caused by unilateral ureteral obstruction
- PMID: 23804447
- PMCID: PMC3761210
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00309.2013
Proximal tubule PPARα attenuates renal fibrosis and inflammation caused by unilateral ureteral obstruction
Abstract
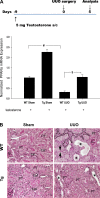
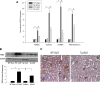
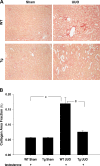
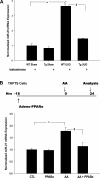
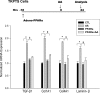
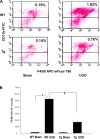
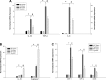
We examined the effects of increased expression of proximal tubule peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)α in a mouse model of renal fibrosis. After 5 days of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO), PPARα expression was significantly reduced in kidney tissue of wild-type mice but this downregulation was attenuated in proximal tubules of PPARα transgenic (Tg) mice. When compared with wild-type mice subjected to UUO, PPARα Tg mice had reduced mRNA and protein expression of proximal tubule transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, with reduced production of extracellular matrix proteins including collagen 1, fibronectin, α-smooth muscle actin, and reduced tubulointerstitial fibrosis. UUO-mediated increased expression of microRNA 21 in kidney tissue was also reduced in PPARα Tg mice. Overexpression of PPARα in cultured proximal tubular cells by adenoviral transduction reduced aristolochic acid-mediated increased production of TGF-β, demonstrating PPARα signaling reduces epithelial TGF-β production. Flow cytometry studies of dissociated whole kidneys demonstrated reduced macrophage infiltration to kidney tissue in PPARα Tg mice after UUO. Increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in wild-type mice was also significantly reduced in kidney tissue of PPARα Tg mice. In contrast, the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and arginase-1 was significantly increased in kidney tissue of PPARα Tg mice when compared with wild-type mice subjected to UUO. Our studies demonstrate several mechanisms by which preserved expression of proximal tubule PPARα reduces tubulointerstitial fibrosis and inflammation associated with obstructive uropathy.
Keywords: interleukin-10; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; transforming growth factor-β.
Figures
References
-
- Boor P, Celec P, Martin IV, Villa L, Hodosy J, Klenovicsova K, Esposito C, Schafer S, Albrecht-Kupper B, Ostendorf T, Heidland A, Sebekova K. The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-[alpha] agonist, BAY PP1, attenuates renal fibrosis in rats. Kidney Int 80: 1182–1197, 2011 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

