T cell-dependent IgM memory B cells generated during bacterial infection are required for IgG responses to antigen challenge
- PMID: 23804710
- PMCID: PMC3720767
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300062
T cell-dependent IgM memory B cells generated during bacterial infection are required for IgG responses to antigen challenge
Abstract
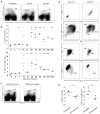
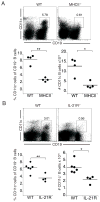
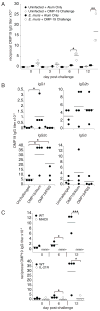
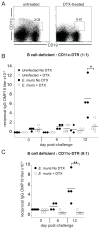
Immunological memory has long considered to be harbored in B cells that express high-affinity class-switched IgG. IgM-positive memory B cells can also be generated following immunization, although their physiological role has been unclear. In this study, we show that bacterial infection elicited a relatively large population of IgM memory B cells that were uniquely identified by their surface expression of CD11c, CD73, and programmed death-ligand 2. The cells lacked expression of cell surface markers typically expressed by germinal center B cells, were CD138 negative, and did not secrete Ab ex vivo. The population was also largely quiescent and accumulated somatic mutations. The IgM memory B cells were located in the region of the splenic marginal zone and were not detected in blood or other secondary lymphoid organs. Generation of the memory cells was CD4 T cell dependent and required IL-21R signaling. In vivo depletion of the IgM memory B cells abrogated the IgG recall responses to specific Ag challenge, demonstrating that the cell population was required for humoral memory, and underwent class-switch recombination following Ag encounter. Our findings demonstrate that T cell-dependent IgM memory B cells can be elicited at high frequency and can play an important role in maintaining long-term immunity during bacterial infection.
Figures


References
-
- McHeyzer-Williams LJ, McHeyzer-Williams MG. Antigen-specific memory B cell development. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:487–513. - PubMed
-
- Kaisho T, Schwenk F, Rajewsky K. The roles of gamma 1 heavy chain membrane expression and cytoplasmic tail in IgG1 responses. Science. 1997;276:412–415. - PubMed
-
- Martin SW, Goodnow CC. Burst-enhancing role of the IgG membrane tail as a molecular determinant of memory. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Tangye SG, Avery DT, Deenick EK, Hodgkin PD. Intrinsic differences in the proliferation of naive and memory human B cells as a mechanism for enhanced secondary immune responses. J Immunol. 2003;170:686–694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

