miR-195 competes with HuR to modulate stim1 mRNA stability and regulate cell migration
- PMID: 23804758
- PMCID: PMC3763549
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt565
miR-195 competes with HuR to modulate stim1 mRNA stability and regulate cell migration
Abstract
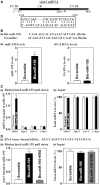
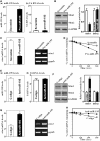
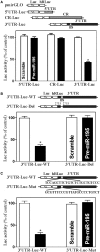
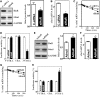
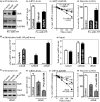
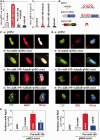
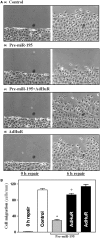
Stromal interaction molecule 1 (Stim1) functions as a sensor of Ca2+ within stores and plays an essential role in the activation of store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE). Although lowering Stim1 levels reduces store-operated Ca2+ entry and inhibits intestinal epithelial repair after wounding, the mechanisms that control Stim1 expression remain unknown. Here, we show that cellular Stim1 abundance is controlled posttranscriptionally via factors that associate with 3'-untranslated region (3'-UTR) of stim1 mRNA. MicroRNA-195 (miR-195) and the RNA-binding protein HuR competed for association with the stim1 3'-UTR and regulated stim1 mRNA decay in opposite directions. Interaction of miR-195 with the stim1 3'-UTR destabilized stim1 mRNA, whereas the stability of stim1 mRNA increased with HuR association. Interestingly, ectopic miR-195 overexpression enhanced stim1 mRNA association with argonaute-containing complexes and increased the colocalization of tagged stim1 RNA with processing bodies (P-bodies); the translocation of stim1 mRNA was abolished by HuR overexpression. Moreover, decreased levels of Stim1 by miR-195 overexpression inhibited cell migration over the denuded area after wounding but was rescued by increasing HuR levels. In sum, Stim1 expression is controlled by two factors competing for influence on stim1 mRNA stability: the mRNA-stabilizing protein HuR and the decay-promoting miR-195.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Polyamines regulate the stability of activating transcription factor-2 mRNA through RNA-binding protein HuR in intestinal epithelial cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2007 Nov;18(11):4579-90. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-07-0675. Epub 2007 Sep 5. Mol Biol Cell. 2007. PMID: 17804813 Free PMC article.
-
Competitive binding of CUGBP1 and HuR to occludin mRNA controls its translation and modulates epithelial barrier function.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jan;24(2):85-99. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-07-0531. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23155001 Free PMC article.
-
miR-519 reduces cell proliferation by lowering RNA-binding protein HuR levels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 23;105(51):20297-302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809376106. Epub 2008 Dec 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19088191 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines regulate the stability of JunD mRNA by modulating the competitive binding of its 3' untranslated region to HuR and AUF1.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;30(21):5021-32. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00807-10. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20805360 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interplay between RNA-binding protein HuR and microRNAs.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Jun;13(4):372-9. doi: 10.2174/138920312801619394. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 22708488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methylxanthines Increase Expression of the Splicing Factor SRSF2 by Regulating Multiple Post-transcriptional Mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jun 12;290(24):14986-5003. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.624254. Epub 2015 Mar 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25818199 Free PMC article.
-
JunD enhances miR-29b levels transcriptionally and posttranscriptionally to inhibit proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 May 15;308(10):C813-24. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00027.2015. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25788572 Free PMC article.
-
miR-195 regulates intestinal epithelial restitution after wounding by altering actin-related protein-2 translation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;322(4):C712-C722. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00001.2022. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35235424 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamines regulate mitochondrial metabolism essential for intestinal epithelial renewal and wound healing.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2025 Jul 1;329(1):G191-G200. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00023.2025. Epub 2025 Jun 5. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40471931 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranscriptional regulation of intestinal epithelial integrity by noncoding RNAs.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Mar;8(2):10.1002/wrna.1399. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1399. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 27704722 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:517–529. - PubMed
-
- Rychkov G, Barritt GJ. TRPC1 Ca2+-permeable channels in animal cells. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2007;179:23–52. - PubMed
-
- Rao JN, Platoshyn O, Golovina VA, Liu L, Zou T, Marasa BS, Turner DJ, Yuan JXJ, Wang Y. TRPC1 functions as a store-operated Ca2+ channel in intestinal epithelial cells and regulates early mucosal restitution after wounding. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G782–G792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

