The eIF2α/ATF4 pathway is essential for stress-induced autophagy gene expression
- PMID: 23804767
- PMCID: PMC3763548
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt563
The eIF2α/ATF4 pathway is essential for stress-induced autophagy gene expression
Abstract
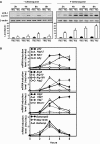
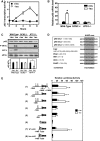
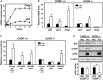
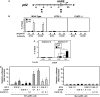
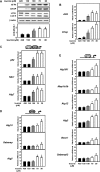
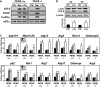
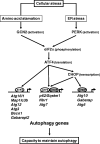
In response to different environmental stresses, eIF2α phosphorylation represses global translation coincident with preferential translation of ATF4, a master regulator controlling the transcription of key genes essential for adaptative functions. Here, we establish that the eIF2α/ATF4 pathway directs an autophagy gene transcriptional program in response to amino acid starvation or endoplasmic reticulum stress. The eIF2α-kinases GCN2 and PERK and the transcription factors ATF4 and CHOP are also required to increase the transcription of a set of genes implicated in the formation, elongation and function of the autophagosome. We also identify three classes of autophagy genes according to their dependence on ATF4 and CHOP and the binding of these factors to specific promoter cis elements. Furthermore, different combinations of CHOP and ATF4 bindings to target promoters allow the trigger of a differential transcriptional response according to the stress intensity. Overall, this study reveals a novel regulatory role of the eIF2α-ATF4 pathway in the fine-tuning of the autophagy gene transcription program in response to stresses.
Figures

References
-
- Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, et al. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:619–633. - PubMed
-
- Wek RC, Jiang HY, Anthony TG. Coping with stress: eIF2 kinases and translational control. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006;34:7–11. - PubMed
-
- Harding HP, Zhang Y, Ron D. Protein translation and folding are coupled by an endoplasmic-reticulum- resident kinase [published erratum appears in Nature 1999 Mar 4;398(6722):90] Nature. 1999;397:271–274. - PubMed
-
- Hinnebusch AG. Mechanism and regulation of intiator methionyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Mathews MB, editors. Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: CSHL Pres; 2000. pp. 185–243.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

