Oxidative stress response signaling pathways in trabecular meshwork cells and their effects on cell viability
- PMID: 23805040
- PMCID: PMC3692401
Oxidative stress response signaling pathways in trabecular meshwork cells and their effects on cell viability
Abstract
Purpose: To clarify the primary oxidative stress response signaling pathways in trabecular meshwork (TM) cells and their effects on cell viability.
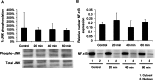
Methods: Porcine TM cells were treated with 600 μM or 800 μM H₂O₂, and their time-dependent morphologic changes were observed. Phosphorylation of protein kinase B (Akt), extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, p38, and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) was evaluated by western blot analysis. The intracellular localization of NFκB was evaluated by western blot analysis. One-hour pretreatments with LY294002, U0126, and SB203580, with the inhibitors of PI3K, ERK1/2, and p38, respectively, were conducted to evaluate the roles of these molecules in the cellular reaction against H₂O₂. Cell viability was assessed using propidium iodide and anticleaved caspase-3 antibody.
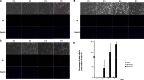
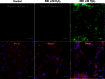
Results: TM cells treated with 600 μM H₂O₂ showed morphologic changes at 2 h that were partially recovered at 8 h after treatment. TM cells treated with 800 μM H₂O₂ did not recover, and the viability was significantly decreased. Both doses of H₂O₂ activated Akt, ERK1/2, and p38 in TM cells at 20 min after treatment, but not JNK or NFкB until 1 h after treatment. Inhibitors of PI3K, ERK1/2, and p38 suppressed recovery from the morphologic changes induced by 600 μM H₂O₂. Of these three inhibitors, the PI3K and ERK1/2 inhibitors decreased TM cell viability under oxidative stress.
Conclusions: In TM cells, the PI3K-Akt, ERK, and p38 signaling pathways are primary oxidative stress response pathways involved in the mechanism of recovery from cellular morphologic changes induced by H₂O₂ treatment accompanied by actin cytoskeletal changes.
Figures




References
-
- Leske MC, Connell AM, Wu SY, Hyman LG, Schachat AP. Risk factors for open-angle glaucoma. The Barbados Eye Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 1995;113:918–24. - PubMed
-
- Leske MC, Heijl A, Hussein M, Bengtsson B, Hyman L, Komaroff E. Factors for glaucoma progression and the effect of treatment: the early manifest glaucoma trial. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121:48–56. - PubMed
-
- Gordon MO, Beiser JA, Brandt JD, Heuer DK, Higginbotham EJ, Johnson CA, Keltner JL, Miller JP, Parrish RK, 2nd, Wilson MR, Kass MA. The Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study: baseline factors that predict the onset of primary open-angle glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2002;120:714–20. - PubMed
-
- Townsend DJ, Brubaker RF. Immediate effect of epinephrine on aqueous formation in the normal human eye as measured by fluorophotometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1980;19:256–66. - PubMed
-
- Jocson VL, Sears ML. Experimental aqueous perfusion in enucleated human eyes. Results after obstruction of Schlemm's canal. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971;86:65–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
