Insulin receptor membrane retention by a traceable chimeric mutant
- PMID: 23805988
- PMCID: PMC3707766
- DOI: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-45
Insulin receptor membrane retention by a traceable chimeric mutant
Abstract
Background: The insulin receptor (IR) regulates glucose homeostasis, cell growth and differentiation. It has been hypothesized that the specific signaling characteristics of IR are in part determined by ligand-receptor complexes localization. Downstream signaling could be triggered from the plasma membrane or from endosomes. Regulation of activated receptor's internalization has been proposed as the mechanism responsible for the differential isoform and ligand-specific signaling.
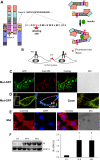
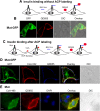
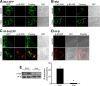
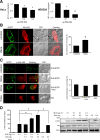
Results: We generated a traceable IR chimera that allows the labeling of the receptor at the cell surface. This mutant binds insulin but fails to get activated and internalized. However, the mutant heterodimerizes with wild type IR inhibiting its auto-phosphorylation and blocking its internalization. IR membrane retention attenuates AP-1 transcriptional activation favoring Akt activation.
Conclusions: These results suggest that the mutant acts as a selective dominant negative blocking IR internalization-mediated signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Subtype-specific regulation of receptor internalization and recycling by the carboxyl-terminal domains of the human A1 and rat A3 adenosine receptors: consequences for agonist-stimulated translocation of arrestin3.Biochemistry. 2002 Dec 17;41(50):14748-61. doi: 10.1021/bi0262911. Biochemistry. 2002. PMID: 12475223
-
Role of the regulatory domain of the EGF-receptor cytoplasmic tail in selective binding of the clathrin-associated complex AP-2.Curr Biol. 1995 Oct 1;5(10):1168-78. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00233-8. Curr Biol. 1995. PMID: 8548289
-
Assessment of insulin proteolysis in rat liver endosomes: its relationship to intracellular insulin signaling.Methods Enzymol. 2014;535:3-23. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397925-4.00001-8. Methods Enzymol. 2014. PMID: 24377914
-
[Involvement of the endosomal compartment in cellular insulin signaling].Biol Aujourdhui. 2014;208(2):137-50. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2014016. Epub 2014 Sep 8. Biol Aujourdhui. 2014. PMID: 25190573 Review. French.
-
Heterodimerization and functional interaction between EGF receptor family members: a new signaling paradigm with implications for breast cancer research.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995 Jul;35(1):115-32. doi: 10.1007/BF00694752. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1995. PMID: 7612898 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin Receptor Trafficking: Consequences for Insulin Sensitivity and Diabetes.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 10;20(20):5007. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205007. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31658625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Physiology and Disease: An Updated View.Endocr Rev. 2017 Oct 1;38(5):379-431. doi: 10.1210/er.2017-00073. Endocr Rev. 2017. PMID: 28973479 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

