Fuz mutant mice reveal shared mechanisms between ciliopathies and FGF-related syndromes
- PMID: 23806618
- PMCID: PMC3697100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.05.021
Fuz mutant mice reveal shared mechanisms between ciliopathies and FGF-related syndromes
Abstract
Ciliopathies are a broad class of human disorders with craniofacial dysmorphology as a common feature. Among these is high arched palate, a condition that affects speech and quality of life. Using the ciliopathic Fuz mutant mouse, we find that high arched palate does not, as commonly suggested, arise from midface hypoplasia. Rather, increased neural crest expands the maxillary primordia. In Fuz mutants, this phenotype stems from dysregulated Gli processing, which in turn results in excessive craniofacial Fgf8 gene expression. Accordingly, genetic reduction of Fgf8 ameliorates the maxillary phenotypes. Similar phenotypes result from mutation of oral-facial-digital syndrome 1 (Ofd1), suggesting that aberrant transcription of Fgf8 is a common feature of ciliopathies. High arched palate is also a prevalent feature of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) hyperactivation syndromes. Thus, our findings elucidate the etiology for a common craniofacial anomaly and identify links between two classes of human disease: FGF-hyperactivation syndromes and ciliopathies.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


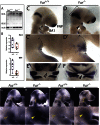

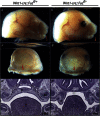


References
-
- Anderson P.J., Hall C., Evans R.D., Harkness W.J., Hayward R.D., Jones B.M. The cervical spine in Crouzon syndrome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1997;22:402–405. - PubMed
-
- Aoto K., Nishimura T., Eto K., Motoyama J. Mouse GLI3 regulates Fgf8 expression and apoptosis in the developing neural tube, face, and limb bud. Dev. Biol. 2002;251:320–332. - PubMed
-
- Arts H.H., Bongers E.M., Mans D.A., van Beersum S.E., Oud M.M., Bolat E., Spruijt L., Cornelissen E.A., Schuurs-Hoeijmakers J.H., de Leeuw N. C14ORF179 encoding IFT43 is mutated in Sensenbrenner syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2011;48:390–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 261299/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- R01 ES020619/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/E013872/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/I021922/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 HD067244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076465/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32DE023272/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DE023272/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- ES020619/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- NS076465/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- G0900867/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HD067244/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

