Regulation of miRNA expression by low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT)
- PMID: 23807510
- PMCID: PMC3742202
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms140713542
Regulation of miRNA expression by low-level laser therapy (LLLT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT)
Abstract
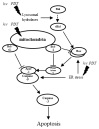
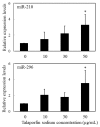
Applications of laser therapy, including low-level laser therapy (LLLT), phototherapy and photodynamic therapy (PDT), have been proven to be beneficial and relatively less invasive therapeutic modalities for numerous diseases and disease conditions. Using specific types of laser irradiation, specific cellular activities can be induced. Because multiple cellular signaling cascades are simultaneously activated in cells exposed to lasers, understanding the molecular responses within cells will aid in the development of laser therapies. In order to understand in detail the molecular mechanisms of LLLT and PDT-related responses, it will be useful to characterize the specific expression of miRNAs and proteins. Such analyses will provide an important source for new applications of laser therapy, as well as for the development of individualized treatments. Although several miRNAs should be up- or down-regulated upon stimulation by LLLT, phototherapy and PDT, very few published studies address the effect of laser therapy on miRNA expression. In this review, we focus on LLLT, phototherapy and PDT as representative laser therapies and discuss the effects of these therapies on miRNA expression.
Figures
References
-
- Maiman T.H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby. Nature. 1960;187:493–494.
-
- Khatri K.A., Mahoney D.L., McCartney M.J. Laser scar revision: A review. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2011;13:54–62. - PubMed
-
- Chung S.H., Mazur E. Surgical applications of femtosecond lasers. J. Biophotonics. 2009;2:557–572. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Z., Wu F. Minimally-invasive thermal ablation of early-stage breast cancer: A systemic review. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010;36:1149–1155. - PubMed
-
- Siribumrungwong B., Noorit P., Wilasrusmee C., Attia J., Thakkinstian A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials comparing endovenous ablation and surgical intervention in patients with varicose vein. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2012;44:214–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

