Alternative sources of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine microalgae
- PMID: 23807546
- PMCID: PMC3736422
- DOI: 10.3390/md11072259
Alternative sources of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine microalgae
Abstract
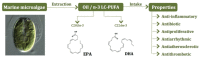
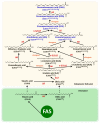
The main source of n-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFA) in human nutrition is currently seafood, especially oily fish. Nonetheless, due to cultural or individual preferences, convenience, geographic location, or awareness of risks associated to fatty fish consumption, the intake of fatty fish is far from supplying the recommended dietary levels. The end result observed in most western countries is not only a low supply of n-3 LC-PUFA, but also an unbalance towards the intake of n-6 fatty acids, resulting mostly from the consumption of vegetable oils. Awareness of the benefits of LC-PUFA in human health has led to the use of fish oils as food supplements. However, there is a need to explore alternatives sources of LC-PUFA, especially those of microbial origin. Microalgae species with potential to accumulate lipids in high amounts and to present elevated levels of n-3 LC-PUFA are known in marine phytoplankton. This review focuses on sources of n-3 LC-PUFA, namely eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids, in marine microalgae, as alternatives to fish oils. Based on current literature, examples of marketed products and potentially new species for commercial exploitation are presented.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microbial and genetically engineered oils as replacements for fish oil in aquaculture feeds.Biotechnol Lett. 2017 Nov;39(11):1599-1609. doi: 10.1007/s10529-017-2402-6. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Biotechnol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28721583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Jumping on the omega-3 bandwagon: distinguishing the role of long-chain and short-chain omega-3 fatty acids.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(9):795-803. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2010.509553. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22698270 Review.
-
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids by Schizochytrium (Aurantiochytrium) spp.Biotechnol Adv. 2022 Mar-Apr;55:107897. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107897. Epub 2021 Dec 30. Biotechnol Adv. 2022. PMID: 34974158 Review.
-
Alternative sources of omega-3 fats: can we find a sustainable substitute for fish?Nutrients. 2013 Apr 18;5(4):1301-15. doi: 10.3390/nu5041301. Nutrients. 2013. PMID: 23598439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative study of tissue deposition of omega-3 fatty acids from polar-lipid rich oil of the microalgae Nannochloropsis oculata with krill oil in rats.Food Funct. 2015 Jan;6(1):186-92. doi: 10.1039/c4fo00591k. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Food Funct. 2015. PMID: 25360534
Cited by
-
Functions of Enyolreductase (ER) Domains of PKS Cluster in Lipid Synthesis and Enhancement of PUFAs Accumulation in Schizochytrium limacinum SR21 Using Triclosan as a Regulator of ER.Microorganisms. 2020 Feb 21;8(2):300. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8020300. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32098234 Free PMC article.
-
Heterotrophic Production of Omega-3 Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids by Trophically Converted Marine Diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum.Mar Drugs. 2016 Mar 9;14(3):53. doi: 10.3390/md14030053. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27005636 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolome response to anthropogenic contamination on microalgae: a review.Metabolomics. 2019 Dec 21;16(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s11306-019-1628-9. Metabolomics. 2019. PMID: 31863210 Review.
-
Host- and Microbe-Dependent Dietary Lipid Metabolism in the Control of Allergy, Inflammation, and Immunity.Front Nutr. 2019 Apr 10;6:36. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00036. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31024921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing EPA Content in an Arctic Diatom: A Factorial Design Study to Evaluate Interactive Effects of Growth Factors.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Apr 17;9:491. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00491. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29755487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mimouni V., Ulmann L., Pasquet V., Mathieu M., Picot L., Bougaran G., Cadoret J.-P., Morant-Manceau A., Schoefs B. The potential of microalgae for the production of bioactive molecules of pharmaceutical interest. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012;13:2733–2750. doi: 10.2174/138920112804724828. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mata T.M., Martins A.A., Caetano N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2010;14:217–232. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.020. - DOI
-
- Kainz M.J., Fisk A.T. Integrating Lipids and Contaminants in Aquatic Ecology and Ecotoxicology. In: Arts M.T., Brett M.T., Kainz M., editors. Lipids in Aquatic Ecosystems. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2009. pp. 93–114.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

