Fibrosing mediastinitis: an unusual cause of pulmonary symptoms
- PMID: 23807725
- PMCID: PMC3832713
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-013-2528-8
Fibrosing mediastinitis: an unusual cause of pulmonary symptoms
Abstract
Fibrosing mediastinitis (FM), also known as granulomatous or sclerosing mediastinitis, is an uncommon but serious cause of chest symptoms. Due to an infectious or inflammatory challenge, production of collagen occurs in the confined space of the mediastinum. Collagen formation leads to compression of vital structures, resulting in cough, chest pain and dyspnea. The majority of cases of FM occur as a result of prior exposure to Histoplasma capsulatum. The following is a case of a previously healthy young woman who presented with a 3-month history of cough, chest pain and trouble breathing, and was subsequently found to have fibrosing mediastinitis. Fibrosing mediastinitis should be considered in the differential diagnosis of cough, chest pain and dyspnea, primarily when findings such as increased venous pressure are present on physical exam and hilar abnormalities are seen on chest radiograph. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and management of fibrosing mediastinitis are discussed.
Figures
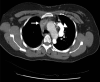
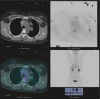
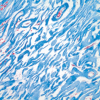
References
-
- NCHS. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. 2010 outpatient department summary tables. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/nhamcs_outpatient/2010_opd_web_tables.pdf Accessed 24 February 2013.
-
- NCHS. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2010 emergency department summary tables. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/nhamcs_emergency/2010_ed_web_tables.pdf Accessed 24 February 2013.
-
- NCHS. National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2010 summary tables. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/ahcd/nhamcs_summary/outpatieny/2010_opd_web... Accessed 24 February 2013.
-
- Loyd JE, Tillman BF, Atkinson JB, Desprez RM. Mediastinal fibrosis complicating histoplasmosis. Medicine. 1998;67:295–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

