Optical ray tracing-guided myopic laser in situ keratomileusis: 1-year clinical outcomes
- PMID: 23807835
- PMCID: PMC3686246
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S44720
Optical ray tracing-guided myopic laser in situ keratomileusis: 1-year clinical outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the safety, efficacy, and predictability of laser in situ keratomileusis treatments at 1 year postprocedure using a novel geometric ray tracing algorithm with outcomes of treatments using wavefront-optimized, wavefront-guided, and topography-guided ablation profiles of an excimer laser (WaveLight GmbH, Erlangen, Germany; Alcon Laboratories, Fort Worth, TX, USA).
Setting: Wellington Eye Clinic, Dublin, Ireland.
Design: Retrospective comparative case series.
Methods: Eyes having a preoperative myopic spherical equivalent refractive error >4.00 D and/or astigmatism between 2.00-6.00 D resulting in a spherical equivalent power greater than -4.00 D received laser in situ keratomileusis treatments using a ray tracing algorithm. Refractive outcomes were analyzed postoperatively at 6 and 12 months and were compared to outcomes of wavefront-optimized, wavefront-guided, and topography-guided treatments in eyes with the same pretreatment refractive range.
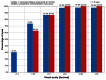
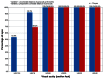
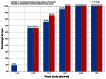
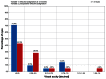
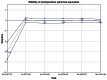
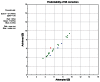
Results: Forty-seven eyes of 26 patients were treated using the ray tracing algorithm. At 12 months postprocedure, uncorrected visual acuity was better than the preoperative best-corrected visual acuity in this group. The percentage of eyes achieving an uncorrected visual acuity or best-corrected visual acuity ≥20/20 significantly exceeded the rates achieved in the wavefront-optimized and topography-guided groups. A greater percentage of eyes achieved an uncorrected visual acuity ≥20/20 and ≥20/16 in the wavefront-guided group, but no eyes in the wavefront-guided group had an uncorrected visual acuity ≥20/12.5 in comparison to 9.5% of eyes in the ray tracing group.
Conclusion: This study provides further evidence of the safety, efficacy, and predictability of laser in situ keratomileusis outcomes using an optical ray tracing algorithm to treat moderate to high myopic astigmatism and shows that good results are sustained through 1 year.
Keywords: Gullstrand eye model; LASIK; ablation profiles; optical ray tracing; topography-guided; wavefront-guided; wavefront-optimized.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Optical ray tracing-guided laser in situ keratomileusis for moderate to high myopic astigmatism.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012 Jan;38(1):28-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2011.06.032. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012. PMID: 22033124
-
Prospective Intraindividual Comparison of Automated Customized Ray-Tracing-Guided versus Wavefront-Optimized LASIK.Ophthalmology. 2025 Jun 5:S0161-6420(25)00341-0. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2025.05.025. Online ahead of print. Ophthalmology. 2025. PMID: 40482723
-
Wavefront-guided versus wavefront-optimized laser in situ keratomileusis for patients with myopia: a prospective randomized contralateral eye study.Am J Ophthalmol. 2014 Jun;157(6):1170-1178.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.02.037. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24560995 Clinical Trial.
-
A Randomized Comparative Study of Topography-Guided Versus Wavefront-Optimized FS-LASIK for Correcting Myopia and Myopic Astigmatism.J Refract Surg. 2019 Sep 1;35(9):575-582. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20190819-01. J Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 31498415 Clinical Trial.
-
Topography-guided versus wavefront-optimized laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia: Surgical outcomes.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2019 Jul;45(7):959-965. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrs.2019.01.031. Epub 2019 Jun 10. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2019. PMID: 31196580
Cited by
-
Initial Outcomes with Customized Myopic LASIK, Guided by Automated Ray Tracing Optimization: A Novel Technique.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov 17;14:3955-3963. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S280560. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33239861 Free PMC article.
-
Ray-Tracing Customization in Myopic and Myopic Astigmatism LASIK Treatments for Low and High Order Aberrations Treatment: 2-Year Visual Function and Psychometric Value Outcomes of a Consecutive Case Series.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Feb 22;18:565-574. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S444174. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38410630 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and Causation of All Inaccurate Outcomes After WaveLight Contoura LASIK with LYRA Protocol.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov 13;14:3841-3854. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S267091. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33223821 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Affecting Ray Trace LASIK Data Acquisition in Clinical Practice: Options for Addressing Accommodation.Clin Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul 3;19:2079-2089. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S524774. eCollection 2025. Clin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40625637 Free PMC article.
-
Current paradigms in refractive surgery.Med J Armed Forces India. 2024 Sep-Oct;80(5):497-504. doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2024.08.003. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Med J Armed Forces India. 2024. PMID: 39309588 Review.
References
-
- Mrochen M, Bueeler M, Donitzky C, Seiler T. Optical ray tracing for the calculation of optimized corneal ablation profiles in refractive treatment planning. J Refract Surg. 2008;24(4):S446–S451. - PubMed
-
- Schumacher S, Seiler T, Cummings A, Maus M, Mrochen M. Optical ray tracing-guided laser in situ keratomileusis for moderate to high myopic astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38(1):28–34. - PubMed
-
- Molebny VV, Panagopoulou SI, Molebny SV, Wakil YS, Pallikaris IG. Principles of ray tracing aberrometry. J Refract Surg. 2000;16(5):S572–S575. - PubMed
-
- Roberts C. Future challenges to aberration-free ablative procedures. J Refract Surg. 2000;16(5):S623–S629. - PubMed
-
- Roberts C. The cornea is not a piece of plastic. J Refract Surg. 2000;16(4):407–413. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

