Mechanisms of reovirus bloodstream dissemination
- PMID: 23809919
- PMCID: PMC4603565
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-407698-3.00001-6
Mechanisms of reovirus bloodstream dissemination
Abstract
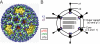
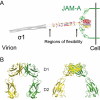
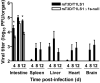
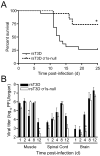
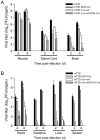
Many viruses cause disease within an infected host after spread from an initial portal of entry to sites of secondary replication. Viruses can disseminate via the bloodstream or through nerves. Mammalian orthoreoviruses (reoviruses) are neurotropic viruses that use both bloodborne and neural pathways to spread systemically within their hosts to cause disease. Using a robust mouse model and a dynamic reverse genetics system, we have identified a viral receptor and a viral nonstructural protein that are essential for hematogenous reovirus dissemination. Junctional adhesion molecule-A (JAM-A) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily expressed in tight junctions and on hematopoietic cells that serves as a receptor for all reovirus serotypes. Expression of JAM-A is required for infection of endothelial cells and development of viremia in mice, suggesting that release of virus into the bloodstream from infected endothelial cells requires JAM-A. Nonstructural protein σ1s is implicated in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in reovirus-infected cells but is completely dispensable for reovirus replication in cultured cells. Surprisingly, a recombinant σ1s-null reovirus strain fails to spread hematogenously in infected mice, suggesting that σ1s facilitates apoptosis of reovirus-infected intestinal epithelial cells. It is possible that apoptotic bodies formed as a consequence of σ1s expression lead to reovirus uptake by dendritic cells for subsequent delivery to the mesenteric lymph node and the blood. Thus, both host and viral factors are required for efficient hematogenous dissemination of reovirus. Understanding mechanisms of reovirus bloodborne spread may shed light on how microbial pathogens invade the bloodstream to disseminate and cause disease in infected hosts.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
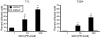
Similar articles
-
Nonstructural Protein σ1s Is Required for Optimal Reovirus Protein Expression.J Virol. 2018 Mar 14;92(7):e02259-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02259-17. Print 2018 Apr 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29321319 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial JAM-A promotes reovirus viremia and bloodstream dissemination.J Infect Dis. 2015 Feb 1;211(3):383-93. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu476. Epub 2014 Aug 22. J Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 25149763 Free PMC article.
-
Junctional adhesion molecule-A is required for hematogenous dissemination of reovirus.Cell Host Microbe. 2009 Jan 22;5(1):59-71. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2008.12.001. Cell Host Microbe. 2009. PMID: 19154988 Free PMC article.
-
Reovirus receptors, cell entry, and proapoptotic signaling.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;790:42-71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-7651-1_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23884585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reoviruses and the host cell.Trends Microbiol. 2001 Nov;9(11):560-4. doi: 10.1016/s0966-842x(01)02103-5. Trends Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11825717 Review.
Cited by
-
Spatiotemporal transcriptomics reveals pathogenesis of viral myocarditis.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Oct;1(10):946-960. doi: 10.1038/s44161-022-00138-1. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 36970396 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-Infected Human Mast Cells Enhance Natural Killer Cell Functions.J Innate Immun. 2017;9(1):94-108. doi: 10.1159/000450576. Epub 2016 Nov 3. J Innate Immun. 2017. PMID: 27806369 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial mapping of the total transcriptome by in situ polyadenylation.Nat Biotechnol. 2023 Apr;41(4):513-520. doi: 10.1038/s41587-022-01517-6. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Nat Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36329320 Free PMC article.
-
Tight Junctions Go Viral!Viruses. 2015 Sep 23;7(9):5145-54. doi: 10.3390/v7092865. Viruses. 2015. PMID: 26404354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteria and bacterial envelope components enhance mammalian reovirus thermostability.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Dec 6;13(12):e1006768. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006768. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 29211815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adair RA, Roulstone V, Scott KJ, Morgan R, Nuovo GJ, Fuller M, Beirne D, West EJ, Jennings VA, Rose A, Kyula J, Fraser S, Dave R, Anthoney DA, Merrick A, Prestwich R, Aldouri A, Donnelly O, Pandha H, Coffey M, Selby P, Vile R, Toogood G, Harrington K, Melcher AA. Cell carriage, delivery, and selective replication of an oncolytic virus in tumor in patients. Science translational medicine. 2012;4:138ra177. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Armstrong GD, Paul RW, Lee PW. Studies on reovirus receptors of L cells: virus binding characteristics and comparison with reovirus receptors of erythrocytes. Virology. 1984;138:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Barratt-Boyes SM, MacLachlan NJ. Dynamics of viral spread in bluetongue virus infected calves. Vet. Microbiol. 1994;40:361–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

