Alpha-actinin 4 and tumorigenesis of breast cancer
- PMID: 23810014
- PMCID: PMC4143506
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00005-8
Alpha-actinin 4 and tumorigenesis of breast cancer
Abstract
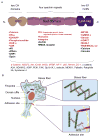
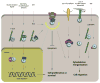
Alpha-actinins (ACTNs) were originally identified as cytoskeletal proteins which cross-link filamentous actin to establish cytoskeletal architect that protects cells from mechanical stress and controls cell movement. Notably, unlike other ACTNs, alpha-actinin 4 (ACTN4) displays unique characteristics in signaling transduction, nuclear translocation, and gene expression regulation. Initial reports indicated that ACTN4 is part of the breast cancer cell motile apparatus and is highly expressed in the nucleus. These results imply that ACTN4 plays a role in breast cancer tumorigenesis. While several observations in breast cancer and other cancers support this hypothesis, little direct evidence links the tumorigenic phenotype with ACTN4-mediated pathological mechanisms. Recently, several studies have demonstrated that in addition to its role in coordinating cytoskeleton, ACTN4 interacts with signaling mediators, chromatin remodeling factors, and transcription factors including nuclear receptors. Thus, ACTN4 functions as a versatile promoter for breast cancer tumorigenesis and appears to be an ideal drug target for future therapeutic development.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The actin-binding protein, actinin alpha 4 (ACTN4), is a nuclear receptor coactivator that promotes proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 21;286(3):1850-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.162107. Epub 2010 Nov 15. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21078666 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear α-actinin-4 regulates breast cancer invasiveness and EMT.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2025 Mar;82(3):145-157. doi: 10.1002/cm.21901. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 39143850
-
Direct inhibition of ACTN4 by ellagic acid limits breast cancer metastasis via regulation of β-catenin stabilization in cancer stem cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 2;36(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0635-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29197410 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ACTN4 in Tumorigenesis, Metastasis, and EMT.Cells. 2019 Nov 13;8(11):1427. doi: 10.3390/cells8111427. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31766144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of KLF5 in hormonal signaling and breast cancer development.Vitam Horm. 2013;93:213-25. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416673-8.00002-2. Vitam Horm. 2013. PMID: 23810009 Review.
Cited by
-
LC-MS/MS Proteomic Study of MCF-7 Cell Treated with Dox and Dox-Loaded Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles Revealed Changes in Proteins Related to Glycolysis, Actin Signalling, and Energy Metabolism.Biology (Basel). 2021 Sep 13;10(9):909. doi: 10.3390/biology10090909. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571787 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of alpha-ACTN4 to EGF receptor enables its rapid phosphorylation.Heliyon. 2021 Jan 21;7(1):e06011. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06011. eCollection 2021 Jan. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33532643 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Cell Adhesion Molecules via Carbonate Apatite-Mediated Delivery of Specific siRNAs to Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Jul 2;11(7):309. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11070309. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31269666 Free PMC article.
-
ACTN4 Promotes the Proliferation, Migration, Metastasis of Osteosarcoma and Enhances its Invasive Ability through the NF-κB Pathway.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Apr;26(2):893-904. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00637-w. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 30879239 Free PMC article.
-
The biological role of actinin-4 (ACTN4) in malignant phenotypes of cancer.Cell Biosci. 2015 Aug 18;5:41. doi: 10.1186/s13578-015-0031-0. eCollection 2015. Cell Biosci. 2015. PMID: 26288717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araki N, Hatae T, Yamada T, Hirohashi S. Actinin-4 is preferentially involved in circular ruffling and macropinocytosis in mouse macrophages: Analysis by fluorescence ratio imaging. Journal of Cell Science. 2000;113:3329–3340. - PubMed
-
- Are AF, Galkin VE, Pospelova TV, Pinaev GP. The p65/RelA subunit of NF-kappaB interacts with actin-containing structures. Experimental Cell Research. 2000;256:533–544. - PubMed
-
- Arimura C, Suzuki T, Yanagisawa M, Imamura M, Hamada Y, Masaki T. Primary structure of chicken skeletal muscle and fibroblast alpha-actinins deduced from cDNA sequences. European Journal of Biochemistry. 1988;177:649–655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

