Accuracy and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF for the diagnosis of smear-negative or sputum-scarce tuberculosis using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- PMID: 23811536
- PMCID: PMC5523966
- DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203485
Accuracy and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF for the diagnosis of smear-negative or sputum-scarce tuberculosis using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
Abstract
Rationale: The accuracy and impact of new tuberculosis (TB) tests, such as Xpert MTB/RIF, when performed on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) obtained from patients with sputum-scarce or smear-negative TB is unclear.
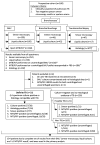
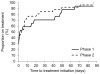
Methods: South African patients with suspected pulmonary TB (n=160) who were sputum-scarce or smear-negative underwent bronchoscopy. MTB/RIF was performed on uncentrifuged BALF (1 ml) and/or a resuspended pellet of centrifuged BALF (∼10 ml). Time to TB detection and anti-TB treatment initiation were compared between phase one, when MTB/RIF was performed as a research tool, and phase two, when it was used for patient management.
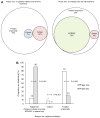
Results: 27 of 154 patients with complete data had culture-confirmed TB. Of these, a significantly lower proportion were detected by smear microscopy compared with MTB/RIF (58%, 95% CI 39% to 75% versus 93%, 77% to 98%; p<0.001). Of the 127 patients who were culture negative, 96% (91% to 98%) were MTB/RIF negative. When phase two was compared with phase one, MTB/RIF reduced the median days to TB detection (29 (18-41) to 0 (0-0); p<0.001). However, more patients initiated empirical therapy (absence of a positive test in those commencing treatment) in phase one versus phase two (79% (11/14) versus 28% (10/25); p=0.026). Consequently, there was no detectable difference in the overall proportion of patients initiating treatment (26% (17/67; 17% to 37%) versus 36% (26/73; 26% to 47%); p=0.196) or the days to treatment initiation (10 (1-49) versus 7 (0-21); p=0.330). BALF centrifugation, HIV coinfection and a second MTB/RIF did not result in detectable changes in accuracy.
Conclusions: MTB/RIF detected TB cases more accurately and more rapidly than smear microscopy and significantly reduced the rate of empirical treatment.
Keywords: Tuberculosis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
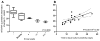

Comment in
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and pulmonary tuberculosis: time to delve deeper?Thorax. 2013 Nov;68(11):987-8. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203885. Epub 2013 Jul 4. Thorax. 2013. PMID: 23828122 No abstract available.
References
-
- Corbett EL, Watt CJ, Walker N, et al. The growing burden of tuberculosis: global trends and interactions with the HIV epidemic. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163:1009. - PubMed
-
- Getahun H, Harrington M, O’Brien R, et al. Diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in people with HIV infection or AIDS in resource-constrained settings: informing urgent policy changes. Lancet. 2007;369:2042–49. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global tuberculosis control 2011. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2011. Publication no. WHO/HTM/TB/2011.16.
-
- Dheda K, Lampe FC, Johnson MA, et al. Outcome of HIV-associated tuberculosis in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:1670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
