Mechanism of eukaryotic RNA polymerase III transcription termination
- PMID: 23812715
- PMCID: PMC3760304
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1237934
Mechanism of eukaryotic RNA polymerase III transcription termination
Abstract
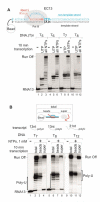
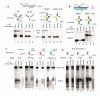
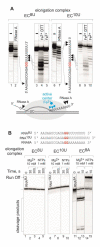
Gene expression in organisms involves many factors and is tightly controlled. Although much is known about the initial phase of transcription by RNA polymerase III (Pol III), the enzyme that synthesizes the majority of RNA molecules in eukaryotic cells, termination is poorly understood. Here, we show that the extensive structure of Pol III-synthesized transcripts dictates the release of elongation complexes at the end of genes. The poly-T termination signal, which does not cause termination in itself, causes catalytic inactivation and backtracking of Pol III, thus committing the enzyme to termination and transporting it to the nearest RNA secondary structure, which facilitates Pol III release. Similarity between termination mechanisms of Pol III and bacterial RNA polymerase suggests that hairpin-dependent termination may date back to the common ancestor of multisubunit RNA polymerases.
Figures
Comment in
-
RNA secondary structure-dependent termination of transcription.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(1):3-4. doi: 10.4161/cc.27018. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24231772 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Transcription. Comment on "Mechanism of eukaryotic RNA polymerase III transcription termination".Science. 2014 Aug 1;345(6196):524. doi: 10.1126/science.1253783. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Science. 2014. PMID: 25082694 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription. Response to Comment on "Mechanism of eukaryotic RNA polymerase III transcription termination".Science. 2014 Aug 1;345(6196):524. doi: 10.1126/science.1254246. Epub 2014 Jul 31. Science. 2014. PMID: 25082695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gusarov I, Nudler E. The mechanism of intrinsic transcription termination. Mol Cell. 1999;3:495. - PubMed
-
- Matsuzaki H, Kassavetis GA, Geiduschek EP. Analysis of RNA chain elongation and termination by Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase III. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 28;235:1173. - PubMed
-
- Bogenhagen DF, Brown DD. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription termination. Cell. 1981 Apr;24:261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

