Cytoplasmic localization of wild-type survivin is associated with constitutive activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and represents a favorable prognostic factor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 23812937
- PMCID: PMC3856963
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2013.083642
Cytoplasmic localization of wild-type survivin is associated with constitutive activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and represents a favorable prognostic factor in patients with acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
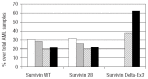
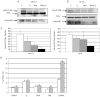
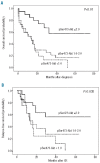
Survivin is over-expressed in most hematologic malignancies but the prognostic significance of the subcompartmental distribution of wild-type or splicing variants in acute myeloid leukemia has not been addressed yet. Using western blotting, we assessed the expression of wild-type survivin and survivin splice variants 2B and Delta-Ex3 in nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts in samples taken from 105 patients at the time of their diagnosis of acute myeloid leukemia. Given that survivin is a downstream effector of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, survivin expression was also correlated with pSer473-Akt. Wild-type survivin and the 2B splice variant were positive in 76.3% and 78.0% of samples in the nucleus, cytoplasm or both, whereas the Delta-Ex3 isoform was only positive in the nucleus in 37.7% of samples. Cytoplasmic localization of wild-type survivin was significantly associated with the presence of high levels of pSer473-Akt (P<0.001). Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway with wortmannin and Ly294002 caused a significant reduction in the expression of cytoplasmic wild-type survivin. The presence of cytoplasmic wild-type survivin and pSer473-Akt was associated with a lower fraction of quiescent leukemia stem cells (P=0.02). The presence of cytoplasmic wild-type survivin and pSer473-Akt were favorable independent prognostic factors. Moreover, the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway with expression of cytoplasmic wild-type survivin identified a subgroup of acute myeloid leukemia patients with an excellent outcome (overall survival rate of 60.0±21.9% and relapse-free survival of 63.0±13.5%). Our findings suggest that cytoplasmic wild-type survivin is a critical downstream effector of the PI3K/Akt pathway leading to more chemosensitive cells and a more favorable outcome in acute myeloid leukemia.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Autocrine IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling is responsible for constitutive PI3K/Akt activation in acute myeloid leukemia: therapeutic value of neutralizing anti-IGF-1R antibody.Haematologica. 2010 Mar;95(3):415-23. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.010785. Epub 2009 Dec 8. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 20007139 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-335/ID4 dysregulation predicts clinical outcome and facilitates leukemogenesis by activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in acute myeloid leukemia.Aging (Albany NY). 2019 May 30;11(10):3376-3391. doi: 10.18632/aging.101991. Aging (Albany NY). 2019. PMID: 31147526 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of constitutive phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in acute myeloid leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(8):2281-8. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2014.990012. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015. PMID: 25426669
-
The PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signaling Pathway in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 21;21(8):2907. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082907. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the PI3K/AKT and mTOR signaling pathways in acute myeloid leukemia.Haematologica. 2010 May;95(5):819-28. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.013797. Epub 2009 Nov 30. Haematologica. 2010. PMID: 19951971 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockout Of BIRC5 Gene By CRISPR/Cas9 Induces Apoptosis And Inhibits Cell Proliferation In Leukemic Cell Lines, HL60 And KG1.Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2019 Nov 27;9:53-61. doi: 10.2147/BLCTT.S230383. eCollection 2019. Blood Lymphat Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31819702 Free PMC article.
-
Survivin splice variants and their diagnostic significance.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(9):6623-31. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3865-5. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 26245993 Review.
-
BIRC5 Gene Disruption via CRISPR/Cas9n Platform Suppress Acute Myelocytic Leukemia Progression.Iran Biomed J. 2019 Nov;23(6):369-78. doi: 10.29252/ibj.23.6.369. Epub 2019 May 20. Iran Biomed J. 2019. PMID: 31104397 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport as a therapeutic target of cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2014 Dec 5;7:85. doi: 10.1186/s13045-014-0085-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25476752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways Affects NRF2, Trx and GSH Antioxidant Systems in Leukemia Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 17;9(7):633. doi: 10.3390/antiox9070633. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32709140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stauber RH, Mann W, Knauer SK. Nuclear and cytoplasmic survivin: molecular mechanism, prognostic and therapeutic potential. Cancer Res. 2007;67(13): 5999–6002 - PubMed
-
- Altieri DC. Survivin, cancer networks and pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(1): 61–70 - PubMed
-
- Caldas H, Jiang Y, Holloway MP, Fangusaro J, Mahotka C, Conway EM, et al. Survivin splice variants regulate the balance between proliferation and cell death. Oncogene. 2005;24(12): 1994–2007 - PubMed
-
- Adida C, Recher C, Raffoux E, Daniel MT, Taksin AL, Rousselot P, et al. Expression and prognostic significance of survivin in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000;111(1): 196–203 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

