Electrical stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve: a potential therapy
- PMID: 23813525
- PMCID: PMC3921355
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00423.2013
Electrical stimulation of the hypoglossal nerve: a potential therapy
Abstract
Obstructive sleep apnea is characterized by recurrent episodes of pharyngeal collapse, which result from a decrease in pharyngeal dilator muscle tone. The genioglossus is a major pharyngeal dilator that maintains airway patency during sleep. Early studies in animal and humans have demonstrated that electrical stimulation of this muscle reduces pharyngeal collapsibility, increases airflow, and mitigates obstructive sleep apnea. These findings impelled the development of fully implantable hypoglossal nerve stimulating systems (HGNS), for which feasibility trial results are now available. These pilot studies have confirmed that hypoglossal nerve stimulation can prevent pharyngeal collapse without arousing patients from sleep. Potentially, a substantial segment of the patient population with obstructive sleep apnea can be treated with this novel approach. Furthermore, the feasibility trial findings suggest that the therapeutic potential of HGNS can be optimized by selecting patients judiciously, titrating the stimulus intensity optimally, and characterizing the underlying function and anatomy of the pharynx. These strategies are currently being examined in ongoing pivotal trials of HGNS.
Keywords: hypoglossal nerve stimulating systems; hypopnea; obstructive sleep apnea; pharyngeal collapse.
Figures

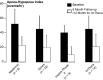
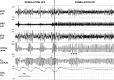
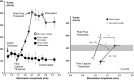
References
-
- Basner RC. Continuous positive airway pressure for obstructive sleep apnea. N Engl J Med 356: 1751–1758, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Decker MJ, Haaga J, Arnold JL, Atzberger D, Strohl KP. Functional electrical stimulation and respiration during sleep. J Appl Physiol 75: 1053–1061, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Dotan Y, Golibroda T, Oliven R, Netzer A, Gaitini L, Toubi A, Oliven A. Parameters affecting pharyngeal response to genioglossus stimulation in sleep apnoea. Eur Respir J 38: 338–347, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Eastwood PR, Barnes M, Walsh JH, Maddison KJ, Hee G, Schwartz AR, Smith PL, Malhotra A, McEvoy RD, Wheatley JR, O'Donoghue FJ, Rochford PD, Churchward T, Campbell MC, Palme CE, Robinson S, Goding GS, Eckert DJ, Jordan AS, Catcheside PG, Tyler L, Antic NA, Worsnop CJ, Kezirian EJ, Hillman DR. Treating obstructive sleep apnea with hypoglossal nerve stimulation. Sleep 34: 1479–1486, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Edmonds LC, Daniels BK, Stanson AW, Sheedy PF, Shepard JWJ. The effects of transcutaneous electrical stimulation during wakefulness and sleep in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am Rev Respir Dis 146: 1030–1036, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

