The duplication 17p13.3 phenotype: analysis of 21 families delineates developmental, behavioral and brain abnormalities, and rare variant phenotypes
- PMID: 23813913
- PMCID: PMC5517092
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35996
The duplication 17p13.3 phenotype: analysis of 21 families delineates developmental, behavioral and brain abnormalities, and rare variant phenotypes
Abstract
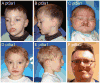
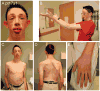
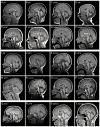
Chromosome 17p13.3 is a gene rich region that when deleted is associated with the well-known Miller-Dieker syndrome. A recently described duplication syndrome involving this region has been associated with intellectual impairment, autism and occasional brain MRI abnormalities. We report 34 additional patients from 21 families to further delineate the clinical, neurological, behavioral, and brain imaging findings. We found a highly diverse phenotype with inter- and intrafamilial variability, especially in cognitive development. The most specific phenotype occurred in individuals with large duplications that include both the YWHAE and LIS1 genes. These patients had a relatively distinct facial phenotype and frequent structural brain abnormalities involving the corpus callosum, cerebellar vermis, and cranial base. Autism spectrum disorders were seen in a third of duplication probands, most commonly in those with duplications of YWHAE and flanking genes such as CRK. The typical neurobehavioral phenotype was usually seen in those with the larger duplications. We did not confirm the association of early overgrowth with involvement of YWHAE and CRK, or growth failure with duplications of LIS1. Older patients were often overweight. Three variant phenotypes included cleft lip/palate (CLP), split hand/foot with long bone deficiency (SHFLD), and a connective tissue phenotype resembling Marfan syndrome. The duplications in patients with clefts appear to disrupt ABR, while the SHFLD phenotype was associated with duplication of BHLHA9 as noted in two recent reports. The connective tissue phenotype did not have a convincing critical region. Our experience with this large cohort expands knowledge of this diverse duplication syndrome.
Keywords: 17p13.3; ABR; BHLHA9; LIS1; YWHAE; autism; cleft lip/palate; marfanoid habitus; microarray; split hand foot long bone deficiency.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures








References
-
- Armour CM, Bulman DE, Jarinova O, Rogers RC, Clarkson KB, DuPont BR, Dwivedi A, Bartel FO, McDonell L, Schwartz CE, Boycott KM, Everman DB, Graham GE. 17p13.3 microduplications are associated with split-hand/foot malformation and long-bone deficiency (SHFLD) Eur J Hum Genet. 2011;19(11):1144–1151. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bi W, Sapir T, Shchelochkov OA, Zhang F, Withers MA, Hunter JV, Levy T, Shinder V, Peiffer DA, Gunderson KL, Nezarati MM, Shotts VA, Amato SS, Savage SK, Harris DJ, Day-Salvatore DL, Horner M, Lu XY, Sahoo T, Yanagawa Y, Beaudet AL, Cheung SW, Martinez S, Lupski JR, Reiner O. Increased LIS1 expression affects human and mouse brain development. Nat Genet. 2009;41(2):168–177. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bruno DL, Anderlid BM, Lindstrand A, van Ravenswaaij-Arts C, Ganesamoorthy D, Lundin J, Martin CL, Douglas J, Nowak C, Adam MP, Kooy RF, Van der Aa N, Reyniers E, Vandeweyer G, Stolte-Dijkstra I, Dijkhuizen T, Yeung A, Delatycki M, Borgstrom B, Thelin L, Cardoso C, van Bon B, Pfundt R, de Vries BB, Wallin A, Amor DJ, James PA, Slater HR, Schoumans J. Further molecular and clinical delineation of co-locating 17p13.3 microdeletions and microduplications that show distinctive phenotypes. J Med Genet. 2010;47(5):299–311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

