Recent advances in the molecular pathogenesis of dystonia-plus syndromes and heredodegenerative dystonias
- PMID: 23814535
- PMCID: PMC3580789
- DOI: 10.2174/157015913804999432
Recent advances in the molecular pathogenesis of dystonia-plus syndromes and heredodegenerative dystonias
Abstract
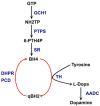
The majority of studies investigating the molecular pathogenesis and cell biology underlying dystonia have been performed in individuals with primary dystonia. This includes monogenic forms such as DYT1and DYT6 dystonia, and primary focal dystonia which is likely to be multifactorial in origin. In recent years there has been renewed interest in non-primary forms of dystonia including the dystonia-plus syndromes and heredodegenerative disorders. These are caused by a variety of genetic mutations and their study has contributed to our understanding of the neuronal dysfunction that leads to dystonia These findings have reinforced themes identified from study of primary dystonia including abnormal dopaminergic signalling, cellular trafficking and mitochondrial function. In this review we highlight recent advances in the understanding of the dystonia-plus syndromes and heredodegenerative dystonias.
Keywords: Dystonia- plus syndrome; Mitochondria.; Molecular pathogenesis; Neurodegeneration; Secondary dystonia.
Figures
References
-
- Phukan J, Albanese A, Gasser T, Warner T. Primary dystonia and dystonia-plus syndromes: clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:1074–1085. - PubMed
-
- Trender-Gerhard I, Sweeney MG, Schwingenschuh P, Mir P, Edwards MJ, Gerhard A, Polke JM, Hanna MG, Davis MB, Wood NW, Bhatia K P. Autosomal-dominant GTPCH1-deficient DRD: clinical characteristics and long-term outcome of 34 patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2009;80:839–845. - PubMed
-
- Van Hove JL, Steyaert J, Matthijs G, Legius E, Theys P, Wevers R, Romstad A, Moller LB, Hedrich K, Goriounov D, Blau N, Klein C, Casaer P. Expanded motor and psychiatric phenotype in autosomal dominant Segawa syndrome due to GTP cyclohydrolase deficiency. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2006;77:18–23. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clot F, Grabli D, Cazeneuve C, Roze E, Castelnau P, Chabrol B, Landrieu P, Nguyen K, Ponsot G, Abada M, Diane D, Philippe D, Roger G, Stéphane T, Alana J W, Michael H, Annick T, Fabienne P, Agnès C, Estelle F, Chankannira S, Delphine B, Eric LeGuern, Alexandra D, Marie V, Alexis B. Exhaustive analysis of BH4 and dopamine biosynthesis genes in patients with Dopa-responsive dystonia. Brain. 2009;132:1753–1763. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa Y, Nygaard TG, Gütlich M, Rajput AH, Pifl C, DiStefano L, Chang LJ, Price K, Shimadzu M, Hornykiewicz O, Haycock JW, Kish SJ. Striatal biopterin and tyrosine hydroxylase protein reduction in dopa-responsive dystonia. Neurology. 1999;53:1032–1041. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
