Decreased A-currents in hippocampal dentate granule cells after seizure-inducing hypoxia in the immature rat
- PMID: 23815572
- PMCID: PMC3703871
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.12150
Decreased A-currents in hippocampal dentate granule cells after seizure-inducing hypoxia in the immature rat
Abstract
Purpose: Cerebral hypoxia is a major cause of neonatal seizures, and can lead to epilepsy. Pathologic anatomic and physiologic changes in the dentate gyrus have been associated with epileptogenesis in many experimental models, as this region is widely believed to gate the propagation of limbic seizures. However, the consequences of hypoxia-induced seizures for the immature dentate gyrus have not been extensively examined.
Methods: Seizures were induced by global hypoxia (5-7% O2 for 15 min) in rat pups on postnatal day 10. Whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings were used to examine A-type potassium currents (IA ) in dentate granule cells in hippocampal slices obtained 1-17 days after hypoxia treatment.
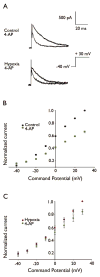
Key findings: Seizure-inducing hypoxia resulted in decreased maximum IA amplitude in dentate granule cells recorded within the first week but not at later times after hypoxia treatment. The decreased IA amplitude was not associated with changes in the voltage-dependence of activation or inactivation removal, or in sensitivity to inhibition by 4-aminopyridine (4-AP). However, consistent with the role of IA in shaping firing patterns, we observed in the hypoxia group a significantly decreased latency to first spike with depolarizing current injection from hyperpolarized potentials. These differences were not associated with changes in resting membrane potential or input resistance, and were eliminated by application of 10 m 4-AP.
Significance: Given the role of IA to slow action potential firing, decreased IA could contribute to long-term hippocampal pathology after neonatal seizure-inducing hypoxia by increasing dentate granule cell excitability during a critical window of activity-dependent hippocampal maturation.
Keywords: A-current; Epilepsy; Hippocampal slice; Patch clamp.
Wiley Periodicals, Inc. © 2013 International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patch-clamp study of postnatal development of CA1 neurons in rat hippocampal slices: membrane excitability and K+ currents.J Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;68(1):55-69. doi: 10.1152/jn.1992.68.1.55. J Neurophysiol. 1992. PMID: 1517828
-
Decreased IH in hippocampal area CA1 pyramidal neurons after perinatal seizure-inducing hypoxia.Epilepsia. 2006 Jun;47(6):1023-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00574.x. Epilepsia. 2006. PMID: 16822248
-
Activation of κ opioid receptors increases intrinsic excitability of dentate gyrus granule cells.J Physiol. 2011 Jul 15;589(Pt 14):3517-32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.211623. Epub 2011 May 23. J Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21606111 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenesis and epilepsy in the developing brain.Epilepsia. 2008 Jun;49 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):50-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01637.x. Epilepsia. 2008. PMID: 18522600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relationship between chronic hypoxia and seizure susceptibility.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Nov;28(11):1689-1705. doi: 10.1111/cns.13942. Epub 2022 Aug 18. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35983626 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Kv4.2 A-Type Potassium Channels in HEK-293 Cells by Hypoxia.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 Oct 14;8:329. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00329. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25352783 Free PMC article.
-
Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Suppresses LPS-Induced Inhibition of A-Type Potassium Channel Currents in Caudate Nucleus Neurons Through CB1 Receptor.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Aug;59(4):493-503. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0761-4. Epub 2016 Apr 29. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27129498
-
Potassium Channels in Epilepsy.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016 May 2;6(5):a022871. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022871. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2016. PMID: 27141079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-485 inhibits histone deacetylase HDAC5, HIF1α and PFKFB3 expression to alleviate epilepsy in cellular and rodent models.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 May 21;13(10):14416-14432. doi: 10.18632/aging.203058. Epub 2021 May 21. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34021541 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia with inflammation and reperfusion alters membrane resistance by dynamically regulating voltage-gated potassium channels in hippocampal CA1 neurons.Mol Brain. 2021 Sep 23;14(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00857-9. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 34556177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aicardi J, Chevrie JJ. Convulsive status epilepticus in infants and children. A study of 239 cases. Epilepsia. 1970;11:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Holmqvist B, Voorhoeve PE. Entorhinal activation of dentate granule cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1966;66:448–460. - PubMed
-
- Bahremand A, Ziai P, Khodadad TK, Payandemehr B, Rahimian R, Ghasemi A, Ghasemi M, Hedayat T, Dehpour AR. Agmatine enhances the anticonvulsant effect of lithium chloride on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in mice: Involvement of L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway. Epilepsy Behav. 2010;18:186–192. - PubMed
-
- Bernard C, Anderson A, Becker A, Poolos NP, Beck H, Johnston D. Acquired dendritic channelopathy in temporal lobe epilepsy. Science. 2004;305:532–535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

