Lung clearance index and high-resolution computed tomography scores in primary ciliary dyskinesia
- PMID: 23815669
- PMCID: PMC3827705
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201304-0800OC
Lung clearance index and high-resolution computed tomography scores in primary ciliary dyskinesia
Abstract
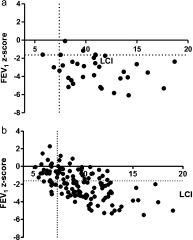
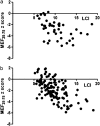
Rationale: Lung clearance index (LCI) is a more sensitive measure of lung function than spirometry in cystic fibrosis (CF) and correlates well with abnormalities in high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scanning. We hypothesized LCI would be equally sensitive to lung disease in primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD).
Objectives: To test the relationships between LCI, spirometry, and HRCT in PCD and to compare them to the established relationships in CF.
Methods: Cross-sectional study of 127 patients with CF and 33 patients with PCD, all of whom had spirometry and LCI, of which a subset of 21 of each had HRCT performed. HRCT was scored for individual features and these features compared with physiological parameters.
Measurements and main results: Unlike in CF, and contrary to our hypothesis, there was no correlation between spirometry and LCI in PCD and no correlation between HRCT features and LCI or spirometry in PCD.
Conclusions: We show for the first time that HRCT, spirometry, and LCI have different relationships in different airway diseases and that LCI does not appear to be a sensitive test of airway disease in advanced PCD. We hypothesize that this results from dissimilarities between the components of large and small airway disease in CF and PCD. These differences may in part lead to the different prognosis in these two neutrophilic airway diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Multiple Breath Washout and Spirometry in Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Cystic Fibrosis and Healthy Controls.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Sep;17(9):1085-1093. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201905-375OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. PMID: 32603187 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple-breath inert gas washout and spirometry versus structural lung disease in cystic fibrosis.Thorax. 2008 Feb;63(2):129-34. doi: 10.1136/thx.2007.077784. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Thorax. 2008. PMID: 17675316
-
Structural and functional lung disease in primary ciliary dyskinesia.Chest. 2008 Aug;134(2):351-357. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-2812. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Chest. 2008. PMID: 18403663
-
A systematic review of lung clearance index in non-cystic fibrosis, non-primary ciliary dyskinesia bronchiectasis.Respir Med. 2022 Sep;201:106937. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106937. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35926429
-
[Lung clearance index in cystic fibrosis].Rev Mal Respir. 2019 Mar;36(3):377-395. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2018.03.007. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Rev Mal Respir. 2019. PMID: 30686561 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Lung Clearance Index (LCI) in Patients with Bronchiolitis Obliterans: A Preliminary Report and Comparison to Cystic Fibrosis Patients.Lung. 2016 Dec;194(6):1007-1013. doi: 10.1007/s00408-016-9934-8. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Lung. 2016. PMID: 27645685
-
Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia: First Health-related Quality-of-Life Measures for Pediatric Patients.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016 Oct;13(10):1726-1735. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201603-198OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016. PMID: 27464304 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Multiple Breath Washout and Spirometry in Children with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia and Cystic Fibrosis and Healthy Controls.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020 Sep;17(9):1085-1093. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201905-375OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2020. PMID: 32603187 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of pediatric health-related quality of life instruments for primary ciliary dyskinesia (QOL-PCD).Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019 Dec;54(12):2011-2020. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24507. Epub 2019 Sep 1. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2019. PMID: 31475479 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and management of primary ciliary dyskinesia.Arch Dis Child. 2014 Sep;99(9):850-6. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304831. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Arch Dis Child. 2014. PMID: 24771309 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bush A, Payne D, Pike S, Jenkins G, Henke MO, Rubin BK. Mucus properties in children with primary ciliary dyskinesia: comparison with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 2006;129:118–123. - PubMed
-
- Noone PG, Leigh MW, Sannuti A, Minnix SL, Carson JL, Hazucha M, Zariwala MA, Knowles MR. Primary ciliary dyskinesia: diagnostic and phenotypic features. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;169:459–467. - PubMed
-
- Zihlif N, Paraskakis E, Lex C, Van de Pohl LA, Bush A. Correlation between cough frequency and airway inflammation in children with primary ciliary dyskinesia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2005;39:551–557. - PubMed
-
- Zihlif N, Paraskakis E, Tripoli C, Lex C, Bush A. Markers of airway inflammation in primary ciliary dyskinesia studied using exhaled breath condensate. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2006;41:509–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

