Defect in recruiting effector memory CD8+ T-cells in malignant pleural effusions compared to normal pleural fluid
- PMID: 23816056
- PMCID: PMC3718618
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-324
Defect in recruiting effector memory CD8+ T-cells in malignant pleural effusions compared to normal pleural fluid
Abstract
Background: Malignant pleural effusions (MPE) are a common and fatal complication in cancers including lung or breast cancers, or malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). MPE animal models and immunotherapy trials in MPM patients previously suggested defects of the cellular immunity in MPE. However only few observational studies of the immune response were done in MPM patients, using questionable control groups (transudate…).
Methods: We compared T cell populations evaluated by flow cytometry from blood and pleural effusion of untreated patients with MPM (n = 58), pleural metastasis of adenocarcinoma (n = 30) or with benign pleural lesions associated with asbestos exposure (n = 23). Blood and pleural fluid were also obtained from healthy subjects, providing normal values for T cell populations.
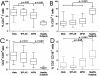
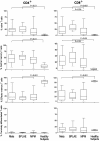
Results: Blood CD4+ or CD8+ T cells percentages were similar in all groups of patients or healthy subjects. Whereas pleural fluid from healthy controls contained mainly CD8+ T cells, benign or malignant pleural effusions included mainly CD4+ T cells. Effector memory T cells were the main T cell subpopulation in pleural fluid from healthy subjects. In contrast, there was a striking and selective recruitment of central memory CD4+ T cells in MPE, but not of effector cells CD8+ T cells or NK cells in the pleural fluid as one would expect in order to obtain an efficient immune response.
Conclusions: Comparing for the first time MPE to pleural fluid from healthy subjects, we found a local defect in recruiting effector CD8+ T cells, which may be involved in the escape of tumor cells from immune response. Further studies are needed to characterize which subtypes of effector CD8+ T cells are involved, opening prospects for cell therapy in MPE and MPM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Flow cytometric study of T-cell subsets in lymphocytic pleural effusions.Cytometry. 1997 Aug 15;30(4):204-5. Cytometry. 1997. PMID: 9298840 No abstract available.
-
Malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions: immunophenotypic cellular characterization.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008 Oct;63(5):637-44. doi: 10.1590/s1807-59322008000500012. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2008. PMID: 18925324 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells and cytokines in malignant pleural effusions secondary to mesothelioma and carcinoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2005 Mar;4(3):342-6. doi: 10.4161/cbt.4.3.1644. Epub 2005 Mar 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15846066
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen in pleural effusions. Diagnostic value in malignant mesothelioma.Cancer. 1984 Mar 1;53(5):1194-7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19840301)53:5<1194::aid-cncr2820530528>3.0.co;2-n. Cancer. 1984. PMID: 6362839 Review.
-
Immune responses and immunotherapeutic interventions in malignant pleural mesothelioma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011 Nov;60(11):1509-27. doi: 10.1007/s00262-011-1103-6. Epub 2011 Sep 13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21913025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin-2 reverses CD8(+) T cell exhaustion in clinical malignant pleural effusion of lung cancer.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Oct;186(1):106-14. doi: 10.1111/cei.12845. Epub 2016 Aug 23. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27447482 Free PMC article.
-
Higher CD4/CD8 ratio of pleural effusion predicts better survival for lung cancer patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;11(1):9381. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89043-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33931705 Free PMC article.
-
Tumour associated lymphocytes in the pleural effusions of patients with mesothelioma express high levels of inhibitory receptors.BMC Res Notes. 2018 Dec 5;11(1):864. doi: 10.1186/s13104-018-3953-x. BMC Res Notes. 2018. PMID: 30518402 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Lymphocyte Immunological Reactivity in Patients with Pleural Effusions of Different Aetiology.Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2016 Mar 15;4(1):50-3. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2016.009. Epub 2015 Dec 25. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27275329 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic Natural Killer Subpopulations as a Prognostic Factor of Malignant Pleural Effusion.Lung. 2019 Feb;197(1):53-60. doi: 10.1007/s00408-018-0186-7. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Lung. 2019. PMID: 30523401
References
-
- Sahn S. In: Pleural disease. Bouros D, editor. London: Informa Healthcare; 2004. Malignant pleural effusions; pp. 411–438.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

