Pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin on the glucose metabolism and the subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue behavior in C57Bl/6 mice
- PMID: 23816341
- PMCID: PMC3716873
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-32
Pleiotropic effects of rosuvastatin on the glucose metabolism and the subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue behavior in C57Bl/6 mice
Abstract
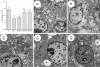
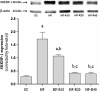
The aim of this study was to evaluate whether rosuvastatin (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor) modulates the carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and the increase in body mass in a model of diet-induced obesity. Male C57Bl/6 mice (3-months-old) were fed a high-fat diet (HF, 60% lipids) or the standard chow (SC, 10% lipids) for 15 weeks. The animals were then treated with 10 mg/kg/day (HF-R10 group), 20 mg/kg/day (HF-R20), or 40 mg/kg/day (HF-R40) of rosuvastatin for five weeks. The HF diet led to glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, weight gain, increased visceral adiposity with adipocyte hypertrophy, and hepatic steatosis (micro and macrovesicular). The rosuvastatin treatment decreased the adiposity and the adipocyte size in the HF-R10 and HF-R20 groups. In addition, rosuvastatin changed the pattern of fat distribution in the HF-R40 group because more fat was stored subcutaneously than in visceral depots. This redistribution improved the fasting glucose and the glucose intolerance. Rosuvastatin also improved the liver morphology and ultrastructure in a dose-dependent manner. In conclusion, rosuvastatin exerts pleiotropic effects through a dose-dependent improvement of glucose intolerance, insulin sensitivity and NAFLD and changes the fat distribution from visceral to subcutaneous fat depots in a mouse model of diet-induced obesity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Weight loss enhances hepatic antioxidant status in a NAFLD model induced by high-fat diet.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018 Jan;43(1):23-29. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2017-0317. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018. PMID: 28834687
-
Fish oil prevents changes induced by a high-fat diet on metabolism and adipokine secretion in mice subcutaneous and visceral adipocytes.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;594(21):6301-6317. doi: 10.1113/JP272541. Epub 2016 Aug 25. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27558442 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of rosuvastatin on insulin resistance, adiposity, inflammatory markers and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice fed on a high-fat diet.Clin Sci (Lond). 2012 Aug 1;123(4):259-70. doi: 10.1042/CS20110373. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012. PMID: 22420611
-
Comparative effects of telmisartan, sitagliptin and metformin alone or in combination on obesity, insulin resistance, and liver and pancreas remodelling in C57BL/6 mice fed on a very high-fat diet.Clin Sci (Lond). 2010 Jun 8;119(6):239-50. doi: 10.1042/CS20100061. Clin Sci (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20415664
-
The inhibitory effect of genistein on hepatic steatosis is linked to visceral adipocyte metabolism in mice with diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.Br J Nutr. 2010 Nov;104(9):1333-42. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510002266. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Br J Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20687969
Cited by
-
Genetic determinants of obesity heterogeneity in type II diabetes.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020 Jul 9;17:55. doi: 10.1186/s12986-020-00476-6. eCollection 2020. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32670384 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of rosuvastatin and/or β-carotene on non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2015 Jul-Aug;10(4):275-87. Res Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 26600855 Free PMC article.
-
Benefit-risk assessment of rosuvastatin in the treatment of atherosclerosis and related diseases.Drug Saf. 2014 Jul;37(7):481-500. doi: 10.1007/s40264-014-0169-4. Drug Saf. 2014. PMID: 24788803 Review.
-
Rosuvastatin Reduces Aortic Sinus and Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis in SR-B1 (Scavenger Receptor Class B Type 1)/ApoE (Apolipoprotein E) Double Knockout Mice Independently of Plasma Cholesterol Lowering.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Jan;38(1):26-39. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.305140. Epub 2017 Nov 21. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29162602 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin reduced brain parasite burden in a chronic toxoplasmosis in vivo model and influenced the neuropathological pattern of ME-49 strain.Parasitology. 2020 Mar;147(3):303-309. doi: 10.1017/S0031182019001604. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Parasitology. 2020. PMID: 31727196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel T. et al.Safety and efficacy of combined ezetimibe/simvastatin treatment and simvastatin monotherapy in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15(12):MS6–MS11. - PubMed
-
- Duvnjak M. et al.Therapy of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: current status. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009;60(Suppl 7):57–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

