ETS factors reprogram the androgen receptor cistrome and prime prostate tumorigenesis in response to PTEN loss
- PMID: 23817021
- PMCID: PMC3737318
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3216
ETS factors reprogram the androgen receptor cistrome and prime prostate tumorigenesis in response to PTEN loss
Abstract
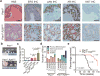
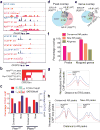
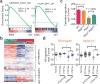
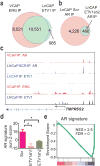
Studies of ETS-mediated prostate oncogenesis have been hampered by a lack of suitable experimental systems. Here we describe a new conditional mouse model that shows robust, homogenous ERG expression throughout the prostate. When combined with homozygous Pten loss, the mice developed accelerated, highly penetrant invasive prostate cancer. In mouse prostate tissue, ERG markedly increased androgen receptor (AR) binding. Robust ERG-mediated transcriptional changes, observed only in the setting of Pten loss, included the restoration of AR transcriptional output and upregulation of genes involved in cell death, migration, inflammation and angiogenesis. Similarly, ETS variant 1 (ETV1) positively regulated the AR cistrome and transcriptional output in ETV1-translocated, PTEN-deficient human prostate cancer cells. In two large clinical cohorts, expression of ERG and ETV1 correlated with higher AR transcriptional output in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer specimens. We propose that ETS factors cause prostate-specific transformation by altering the AR cistrome, priming the prostate epithelium to respond to aberrant upstream signals such as PTEN loss.
Figures


Comment in
-
A step toward functionally characterized prostate cancer molecular subtypes.Nat Med. 2013 Aug;19(8):966-7. doi: 10.1038/nm.3285. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23921739 No abstract available.
-
Prostate tumor development and androgen receptor function alterations in a new mouse model with ERG overexpression and PTEN inactivation.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014 Oct;15(10):1293-5. doi: 10.4161/cbt.29694. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25007053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tomlins SA, et al. Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science. 2005;310:644–648. - PubMed
-
- Tomlins SA, et al. TMPRSS2:ETV4 gene fusions define a third molecular subtype of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3396–3400. - PubMed
-
- Helgeson BE, et al. Characterization of TMPRSS2:ETV5 and SLC45A3:ETV5 gene fusions in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:73–80. - PubMed
-
- Paulo P, et al. FLI1 is a novel ETS transcription factor involved in gene fusions in prostate cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2012;51:240–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

