Origin and function of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis
- PMID: 23817022
- PMCID: PMC4067127
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.3218
Origin and function of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis
Abstract
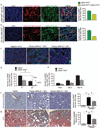
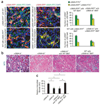
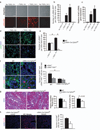
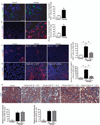
Myofibroblasts are associated with organ fibrosis, but their precise origin and functional role remain unknown. We used multiple genetically engineered mice to track, fate map and ablate cells to determine the source and function of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. Through this comprehensive analysis, we identified that the total pool of myofibroblasts is split, with 50% arising from local resident fibroblasts through proliferation. The nonproliferating myofibroblasts derive through differentiation from bone marrow (35%), the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition program (10%) and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition program (5%). Specific deletion of Tgfbr2 in α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA)(+) cells revealed the importance of this pathway in the recruitment of myofibroblasts through differentiation. Using genetic mouse models and a fate-mapping strategy, we determined that vascular pericytes probably do not contribute to the emergence of myofibroblasts or fibrosis. Our data suggest that targeting diverse pathways is required to substantially inhibit the composite accumulation of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Fibrosis: the source of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013 Sep;9(9):494. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.141. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23877590 No abstract available.
-
The origin of scar-forming kidney myofibroblasts.Nat Med. 2013 Aug;19(8):964-6. doi: 10.1038/nm.3299. Nat Med. 2013. PMID: 23921738 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 CA163191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK55001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK81976/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32DK082119-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA163191/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32DK007726/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32DK007760-11/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA125550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA125550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007726/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007374/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK082119/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32HL007374-30/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

