Cocaine exposure enhances permissiveness of quiescent T cells to HIV infection
- PMID: 23817564
- PMCID: PMC3774841
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1112566
Cocaine exposure enhances permissiveness of quiescent T cells to HIV infection
Abstract
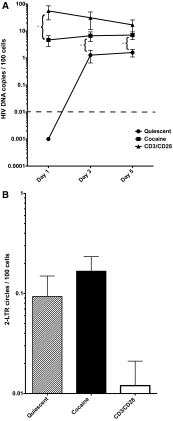
In vivo and in vitro exposure to stimulants has been associated with increased levels of HIV infection in PBMCs. Among these lymphocyte subsets, quiescent CD4(+) T cells make up the majority of circulating T cells in the blood. Others and we have demonstrated that HIV infects this population of cells inefficiently. However, minor changes in their cell state can render them permissive to infection, significantly impacting the viral reservoir. We have hypothesized that stimulants, such as cocaine, may perturb the activation state of quiescent cells enhancing permissiveness to infection. Quiescent T cells isolated from healthy human donors were exposed to cocaine and infected with HIV. Samples were harvested at different time-points to assess the impact of cocaine on their susceptibility to infection at various stages of the HIV life cycle. Our data show that a 3-day exposure to cocaine enhanced infection of quiescent cells, an effect that appears to be mediated by σ1R and D4R. Overall, our results indicate that cocaine-mediated effects on quiescent T cells may increase the pool of infection-susceptible T cells. The latter underscores the impact that stimulants have on HIV-seropositive individuals and the challenges posed for treatment.
Keywords: human immunodeficiency virus; life cycle; reservoir; stimulant abuse; σ1 and D4 receptors.
Figures




References
-
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. (1990) HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell 61, 213–222 - PubMed
-
- Swiggard W. J., O'Doherty U., McGain D., Jeyakumar D., Malim M. H. (2004) Long HIV type 1 reverse transcripts can accumulate stably within resting CD4+ T cells while short ones are degraded. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 20, 285–295 - PubMed
-
- Cole S. W., Jamieson B. D., Zack J. A. (1999) cAMP up-regulates cell surface expression of lymphocyte CXCR4: implications for chemotaxis and HIV-1 infection. J. Immunol. 162, 1392–1400 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

