Elucidating immune mechanisms causing hypertension during pregnancy
- PMID: 23817797
- PMCID: PMC3742131
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00006.2013
Elucidating immune mechanisms causing hypertension during pregnancy
Abstract
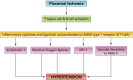
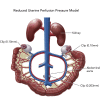
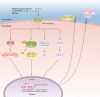
Preeclampsia is associated with hypertension and increased infant and maternal morbidity and mortality. The underlying cause of preeclampsia is largely unknown, but it is clear that an immunological component plays a key pathophysiological role. This review will highlight immunological key players in the pathology of preeclampsia and discuss their role in the pathophysiology observed in the reduced placental perfusion (RUPP) rat model of preeclampsia.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Abbus A, Lichtman A. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. General Properties of the Immune Response, Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2005, p. 163–188
-
- Abbus A, Lichtman A. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. General Properties of the Immune Response, Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2005, p. 189–215
-
- Abbus A, Lichtman A. Cellular and Molecular Immunology. General Properties of the Immune Response, Cells and Tissues of the Immune System. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2005, p. 243–274
-
- Cianchini G, Corona R, Frezzolini A, Ruffelli M, Didona B, Puddu P. Treatment of severe pemphigus with rituximab: report of 12 cases and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol 143: 1033–1038, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Cid MC, Kleinman HK, Grant DS, Schnaper HW, Fauci AS, Hoffman GS. Estradiol enhances leukocyte binding to tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-stimulated endothelial cells via an increase in TNF-induced adhesion molecules E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule type 1, and vascular cell adhesion molecule type 1. J Clin Invest 93: 17–25, 1994 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

