Nutritional lipidomics: molecular metabolism, analytics, and diagnostics
- PMID: 23818328
- PMCID: PMC3806310
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201200808
Nutritional lipidomics: molecular metabolism, analytics, and diagnostics
Abstract
The field of lipidomics is providing nutritional science a more comprehensive view of lipid intermediates. Lipidomics research takes advantage of the increase in accuracy and sensitivity of mass detection of MS with new bioinformatics toolsets to characterize the structures and abundances of complex lipids. Yet, translating lipidomics to practice via nutritional interventions is still in its infancy. No single instrumentation platform is able to solve the varying analytical challenges of the different molecular lipid species. Biochemical pathways of lipid metabolism remain incomplete and the tools to map lipid compositional data to pathways are still being assembled. Biology itself is dauntingly complex and simply separating biological structures remains a key challenge to lipidomics. Nonetheless, the strategy of combining tandem analytical methods to perform the sensitive, high-throughput, quantitative, and comprehensive analysis of lipid metabolites of very large numbers of molecules is poised to drive the field forward rapidly. Among the next steps for nutrition to understand the changes in structures, compositions, and function of lipid biomolecules in response to diet is to describe their distribution within discrete functional compartments lipoproteins. Additionally, lipidomics must tackle the task of assigning the functions of lipids as signaling molecules, nutrient sensors, and intermediates of metabolic pathways.
Keywords: Bile acids; Lipids; Mass spectrometry; Nutrition; Oxylipins.
© 2013 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
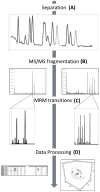
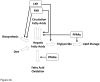



Comment in
-
Lipidomics: approaches and applications in nutrition research.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Aug;57(8):1305. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201370074. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013. PMID: 23913648 No abstract available.
References
-
- Watkins SM, Reifsnyder PR, Pan H-j, German JB, Leiter EH. Lipid metabolome-wide effects of the PPARγ agonist rosiglitazone. Journal of Lipid Research. 2002;43:1809–1817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

