Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance in the intestine
- PMID: 23818502
- PMCID: PMC3685893
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018341
Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance in the intestine
Erratum in
- Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Aug;5(8):a021022
Abstract
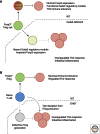
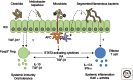
A fundamental role of the mammalian immune system is to eradicate pathogens while minimizing immunopathology. Instigating and maintaining immunological tolerance within the intestine represents a unique challenge to the mucosal immune system. Regulatory T cells are critical for continued immune tolerance in the intestine through active control of innate and adaptive immune responses. Dynamic adaptation of regulatory T-cell populations to the intestinal tissue microenvironment is key in this process. Here, we discuss specialization of regulatory T-cell responses in the intestine, and how a breakdown in these processes can lead to chronic intestinal inflammation.
Figures

References
-
- Barnes MJ, Powrie F 2009. Hybrid Treg cells: Steel frames and plastic exteriors. Nat Immunol 10: 563–564 - PubMed
-
- Bennett CL, Christie J, Ramsdell F, Brunkow ME, Ferguson PJ, Whitesell L, Kelly TE, Saulsbury FT, Chance PF, Ochs HD 2001. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat Genet 27: 20–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
