Monocytes, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and THP-1 cells exhibit different cytokine expression patterns following stimulation with lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 23818743
- PMCID: PMC3681313
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/697972
Monocytes, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and THP-1 cells exhibit different cytokine expression patterns following stimulation with lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
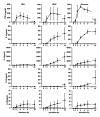
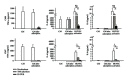
THP-1 cells are widely applied to mimic monocytes in cell culture models. In this study, we compared the cytokine release from THP-1, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), monocytes, or whole blood after stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and investigated the consequences of different cytokine profiles on human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) activation. While Pseudomonas aeruginosa-stimulated (10 ng/mL) THP-1 secreted similar amounts of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF- α ) as monocytes and PBMC, they produced lower amounts of interleukin(IL)-8 and no IL-6 and IL-10. Whole blood required a higher concentration of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (1000 ng/mL) to induce cytokine release than isolated monocytes or PBMC (10 ng/mL). HUVEC secreted more IL-6 and IL-8 after stimulation with conditioned medium derived from whole blood than from THP-1, despite equal concentrations of TNF- α in both media. Specific adsorption of TNF- α or selective cytokine adsorption from the conditioned media prior to HUVEC stimulation significantly reduced HUVEC activation. Our findings show that THP-1 differ from monocytes, PBMC, and whole blood with respect to cytokine release after stimulation with LPS. Additionally, we could demonstrate that adsorption of inflammatory mediators results in reduced endothelial activation, which supports the concept of extracorporeal mediator modulation as supportive therapy for sepsis.
Figures




References
-
- Aird WC. Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium—I. Structure, function, and mechanisms. Circulation Research. 2007;100(2):158–173. - PubMed
-
- Pober JS, Sessa WC. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nature Reviews Immunology. 2007;7(10):803–815. - PubMed
-
- Hack CE, Zeerleder S, Dhainaut JF, Taylor F, Reinhart K. The endothelium in sepsis: source of and a target for inflammation. Critical Care Medicine. 2001;29(7):S21–S27. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda N, Hattori Y. Vascular biology in sepsis: pathophysiological and therapeutic significance of vascular dysfunction. Journal of Smooth Muscle Research. 2007;43(4):117–137. - PubMed
-
- Aird WC. Endothelium in health and disease. Pharmacological Reports. 2008;60(1):139–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

