Effects of respiratory and non-respiratory factors on disability among older adults with airway obstruction: the Cardiovascular Health Study
- PMID: 23819728
- PMCID: PMC3903127
- DOI: 10.3109/15412555.2013.781148
Effects of respiratory and non-respiratory factors on disability among older adults with airway obstruction: the Cardiovascular Health Study
Abstract
Background: High rates of disability associated with chronic airway obstruction may be caused by impaired pulmonary function, pulmonary symptoms, other chronic diseases, or systemic inflammation.
Methods: We analyzed data from the Cardiovascular Health Study, a longitudinal cohort of 5888 older adults. Categories of lung function (normal; restricted; borderline, mild-moderate, and severe obstruction) were delineated by baseline spirometry (without bronchodilator). Disability-free years were calculated as total years alive and without self-report of difficulty performing &γτ;1 Instrumental Activities of Daily Living over 6 years of follow-up. Using linear regression, we compared disability-free years by lung disease category, adjusting for demographic factors, body mass index, smoking, cognition, and other chronic co-morbidities. Among participants with airflow obstruction, we examined the association of respiratory factors (FEV1 and dyspnea) and non-respiratory factors (ischemic heart disease, congestive heart failure, diabetes, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, depression and cognitive impairment) on disability-free years.
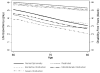
Results: The average disability free years were 4.0 out of a possible 6 years. Severe obstruction was associated with 1 fewer disability-free year compared to normal spirometry in the adjusted model. For the 1,048 participants with airway obstruction, both respiratory factors (FEV1 and dyspnea) and non-respiratory factors (heart disease, coronary artery disease, diabetes, depression, osteoporosis, cognitive function, and weakness) were associated with decreased disability-free years.
Conclusions: Severe obstruction is associated with greater disability compared to patients with normal spirometery. Both respiratory and non-respiratory factors contribute to disability in older adults with abnormal spirometry.
Figures

References
-
- 2009 Chart Book on Cardiovascular, Lung, and Blood Diseases: National Institutes of Health. National Heart Lung and Blood Institute; 2009.
-
- Murphy SL, Xu JQ, Kochanek KD. Deaths: Preliminary Data for 2010. National Center for Health Statistics; Hyattsville, MD: 2012. - PubMed
-
- Iglehart JK. Prioritizing comparative-effectiveness research--IOM recommendations. N Engl J Med. 2009 Jul 23;361(4):325–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG-20098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-027058/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG020098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG027058/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015928/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85239/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
