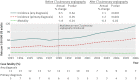
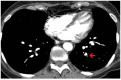
When a test is too good: how CT pulmonary angiograms find pulmonary emboli that do not need to be found
- PMID: 23820021
- PMCID: PMC4688549
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f3368
When a test is too good: how CT pulmonary angiograms find pulmonary emboli that do not need to be found
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the unified competing interest form at
Figures
Comment in
-
Too much medicine; too little care.BMJ. 2013 Jul 2;347:f4247. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f4247. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23820022 No abstract available.
-
The accuracy of CT pulmonary angiography is not as high as purported.BMJ. 2013 Aug 20;347:f5116. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5116. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23963553 No abstract available.
-
CT triple rule-out examination: higher radiation dose without clinical benefit.BMJ. 2013 Aug 20;347:f5118. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5118. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23963554 No abstract available.
-
V/Q SPECT: the primary imaging test for suspected pulmonary embolism.BMJ. 2013 Aug 20;347:f5119. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5119. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23963555 No abstract available.
-
Risk-benefit ratio favours treating all pulmonary emboli, no matter how small.BMJ. 2013 Aug 20;347:f5121. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5121. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23963556 No abstract available.
-
Most patients with isolated subsegmental pulmonary embolism do not need anticoagulants.BMJ. 2013 Aug 20;347:f5127. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5127. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23963557 No abstract available.
-
Authors' reply to Quantrill, Benger, Ripley and colleagues, Roach, Rogers, and Haldar and colleagues.BMJ. 2013 Aug 20;347:f5131. doi: 10.1136/bmj.f5131. BMJ. 2013. PMID: 23963558 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. What is pulmonary embolism? www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/pe/.
-
- Handler JA, Feied CF. Acute pulmonary embolism. Aggressive therapy with anticoagulants and thrombolytics. Postgrad Med 1995;97:61-2, 65-8, 71-2. - PubMed
-
- Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, Stiell I, Dreyer JF, Barnes D, et al. Excluding pulmonary embolism at the bedside without diagnostic imaging: management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism presenting to the emergency department by using a simple clinical model and d-dimer. Ann Intern Med 2001;17;135:98-107. - PubMed
-
- Adams DM, Stevens SM, Woller SC, Evans RS, Lloyd JF, Snow GL, et al. Adherence to PIOPED II investigators’ recommendations for computed tomography pulmonary angiography. Am J Med 2013;126:36-42. - PubMed
-
- Stein PD, Hull RD, Ghali WA, Patel KC, Olson RE, Meyers FA, et al. Tracking the uptake of evidence: two decades of hospital practice trends for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med 2003;163:1213-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical