Elucidating the role of ApxI in hemolysis and cellular damage by using a novel apxIA mutant of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 10
- PMID: 23820218
- PMCID: PMC3973769
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.1.81
Elucidating the role of ApxI in hemolysis and cellular damage by using a novel apxIA mutant of Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 10
Abstract
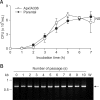
Exotoxins produced by Actinobacillus (A.) pleuropneumoniae (Apx) play major roles in the pathogenesis of pleuropneumonia in swine. This study investigated the role of ApxI in hemolysis and cellular damage using a novel apxIA mutant, ApxIA336, which was developed from the parental strain A. pleuropneumoniae serotype 10 that produces only ApxI in vitro. The genotype of ApxIA336 was confirmed by PCR, Southern blotting, and gene sequencing. Exotoxin preparation derived from ApxIA336 was analyzed for its bioactivity towards porcine erythrocytes and alveolar macrophages. Analysis results indicated that ApxIA336 contained a kanamycin- resistant cassette inserted immediately after 1005 bp of the apxIA gene. Phenotype analysis of ApxIA336 revealed no difference in the growth rate as compared to the parental strain. Meanwhile, ApxI production was abolished in the bacterial culture supernatant, i.e. exotoxin preparation. The inability of ApxIA336 to produce ApxI corresponded to the loss of hemolytic and cytotoxic bioactivity in exotoxin preparation, as demonstrated by hemolysis, lactate dehydrogenase release, mitochondrial activity, and apoptosis assays. Additionally, the virulence of ApxIA336 appeared to be attenuated by 15-fold in BALB/c mice. Collectively, ApxI, but not other components in the exotoxin preparation of A. pleuropneumoniae serotype 10, was responsible for the hemolytic and cytotoxic effects on porcine erythrocytes and alveolar macrophages.
Keywords: Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae; ApxI; attenuation; cytotoxicity; mutant.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TurboID screening of ApxI toxin interactants identifies host proteins involved in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-induced apoptosis of immortalized porcine alveolar macrophages.Vet Res. 2023 Jul 20;54(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01194-6. Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37475032 Free PMC article.
-
Functional and structural changes of porcine alveolar macrophages induced by sublytic doses of a heat-labile, hemolytic, cytotoxic substance produced by Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.Am J Vet Res. 1994 Nov;55(11):1548-57. Am J Vet Res. 1994. PMID: 7879978
-
Mechanisms underlying Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae exotoxin ApxI induced expression of IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α in porcine alveolar macrophages.Vet Res. 2011 Feb 7;42(1):25. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-25. Vet Res. 2011. PMID: 21314908 Free PMC article.
-
New trends in innovative vaccine development against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Apr;217:66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.02.028. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29615259 Review.
-
Virulence factors of the swine pathogen Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae.Microbiologia. 1996 Jun;12(2):171-84. Microbiologia. 1996. PMID: 8767702 Review.
Cited by
-
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae exotoxin ApxI induces cell death via attenuation of FAK through LFA-1.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 18;11(1):1753. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81290-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33462305 Free PMC article.
-
TurboID screening of ApxI toxin interactants identifies host proteins involved in Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-induced apoptosis of immortalized porcine alveolar macrophages.Vet Res. 2023 Jul 20;54(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01194-6. Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37475032 Free PMC article.
-
A Combinatorial Vaccine Containing Inactivated Bacterin and Subunits Provides Protection Against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae Infection in Mice and Pigs.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jun 7;9:902497. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.902497. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35747235 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Immunogenic Potential of ApxI and ApxII from Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae: An Immunoinformatics-Driven Study on mRNA Candidates.Vet Sci. 2025 Apr 27;12(5):414. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12050414. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40431507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiang CH, Huang WF, Huang LP, Lin SF, Yang WJ. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of ApxIA and ApxIIA DNA vaccine against Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae lethal challenge in murine model. Vaccine. 2009;27:4565–4570. - PubMed
-
- Chien MS, Chan YY, Chen ZW, Wu CM, Liao JW, Chen TH, Lee WC, Yeh KS, Hsuan SL. Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae serotype 10 derived ApxI induces apoptosis in porcine alveolar macrophages. Vet Microbiol. 2009;135:327–333. - PubMed
-
- Czuprynski CJ, Welch RA. Biological effects of RTX toxins: the possible role of lipopolysaccharide. Trends Microbiol. 1995;3:480–483. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

