Hollow microporous organic capsules
- PMID: 23820511
- PMCID: PMC3699813
- DOI: 10.1038/srep02128
Hollow microporous organic capsules
Abstract
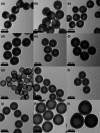
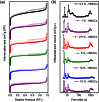
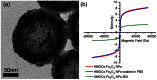
Fabrication of hollow microporous organic capsules (HMOCs) could be very useful because of their hollow and porous morphology, which combines the advantages of both microporous organic polymers and non-porous nanocapsules. They can be used as storage materials or reaction chambers while supplying the necessary path for the design of controlled uptake/release systems. Herein, the synthesis of HMOCs with high surface area through facile emulsion polymerization and hypercrosslinking reactions, is described. Due to their tailored porous structure, these capsules possessed high drug loading efficiency, zero-order drug release kinetics and are also demonstrated to be used as nanoscale reactors for the prepareation of nanoparticles (NPs) without any external stabilizer. Moreover, owing to their intrinsic biocompatibility and fluorescence, these capsules exhibit promising prospect for biomedical applications.
Figures



References
-
- Furukawa H. & Yaghi O. M. Storage of Hydrogen, Methane, and Carbon Dioxide in Highly Porous Covalent Organic Frameworks for Clean Energy Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 8875–8883 (2009). - PubMed
-
- McKeown N. B. et al. Towards Polymer-Based Hydrogen Storage Materials: Engineering Ultramicroporous Cavities within Polymers of Intrinsic Microporosity. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 118, 1836–1839 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Wood C. D. et al. Microporous organic polymers for methane storage. Adv. Mater. 20, 1916–1921 (2008).
-
- Li B., Huang X., Liang L. & Tan B. Synthesis of uniform microporous polymer nanoparticles and their applications for hydrogen storage. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 7444–7450 (2010).
-
- Holst J. R. & Cooper A. I. Ultrahigh Surface Area in Porous Solids. Adv. Mater. 22, 5212–5216 (2010). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

