Where genotype is not predictive of phenotype: towards an understanding of the molecular basis of reduced penetrance in human inherited disease
- PMID: 23820649
- PMCID: PMC3778950
- DOI: 10.1007/s00439-013-1331-2
Where genotype is not predictive of phenotype: towards an understanding of the molecular basis of reduced penetrance in human inherited disease
Abstract
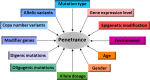
Some individuals with a particular disease-causing mutation or genotype fail to express most if not all features of the disease in question, a phenomenon that is known as 'reduced (or incomplete) penetrance'. Reduced penetrance is not uncommon; indeed, there are many known examples of 'disease-causing mutations' that fail to cause disease in at least a proportion of the individuals who carry them. Reduced penetrance may therefore explain not only why genetic diseases are occasionally transmitted through unaffected parents, but also why healthy individuals can harbour quite large numbers of potentially disadvantageous variants in their genomes without suffering any obvious ill effects. Reduced penetrance can be a function of the specific mutation(s) involved or of allele dosage. It may also result from differential allelic expression, copy number variation or the modulating influence of additional genetic variants in cis or in trans. The penetrance of some pathogenic genotypes is known to be age- and/or sex-dependent. Variable penetrance may also reflect the action of unlinked modifier genes, epigenetic changes or environmental factors. At least in some cases, complete penetrance appears to require the presence of one or more genetic variants at other loci. In this review, we summarize the evidence for reduced penetrance being a widespread phenomenon in human genetics and explore some of the molecular mechanisms that may help to explain this enigmatic characteristic of human inherited disease.
Figures
References
-
- Abifadel M, Rabès JP, Jambart S, Halaby G, Gannagé-Yared MH, Sarkis A, Beaino G, Varret M, Salem N, Corbani S, Aydénian H, Junien C, Munnich A, Boileau C. The molecular basis of familial hypercholesterolemia in Lebanon: spectrum of LDLR mutations and role of PCSK9 as a modifier gene. Hum Mutat. 2009;30:E682–E691. doi: 10.1002/humu.21002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abu-Safieh L, Al-Anazi S, Al-Abdi L, Hashem M, Alkuraya H, Alamr M, Sirelkhatim MO, Al-Hassnan Z, Alkuraya B, Mohamed JY, Al-Salem A, Alrashed M, Faqeih E, Softah A, Al-Hashem A, Wali S, Rahbeeni Z, Alsayed M, Khan AO, Al-Gazali L, Taschner PE, Al-Hazzaa S, Alkuraya FS. In search of triallelism in Bardet–Biedl syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2012;20:420–427. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2011.205. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ackermann B, Kröber S, Torres-Benito L, Borgmann A, Peters M, Hosseini Barkooie SM, Tejero R, Jakubik M, Schreml J, Milbradt J, Wunderlich TF, Riessland M, Tabares L, Wirth B. Plastin 3 ameliorates spinal muscular atrophy via delayed axon pruning and improves neuromuscular junction functionality. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22:1328–1347. doi: 10.1093/hmg/dds540. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aganna E, Aksentijevich I, Hitman GA, Kastner DL, Hoepelman AI, Posma FD, Zweers EJ, McDermott MF. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) in a Dutch family: evidence for a TNFRSF1A mutation with reduced penetrance. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001;9:63–66. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200573. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical