Determinants of the heightened activity of glucocorticoid receptor translational isoforms
- PMID: 23820903
- PMCID: PMC3753425
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2013-1009
Determinants of the heightened activity of glucocorticoid receptor translational isoforms
Abstract
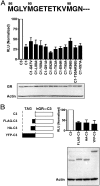
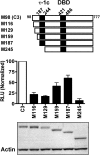
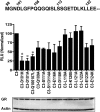
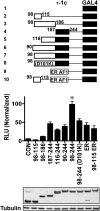
Translational isoforms of the glucocorticoid receptor α (GR-A, -B, -C1, -C2, -C3, -D1, -D2, and -D3) have distinct tissue distribution patterns and unique gene targets. The GR-C3 isoform-expressing cells are more sensitive to glucocorticoid killing than cells expressing other GRα isoforms and the GR-D isoform-expressing cells are resistant to glucocorticoid killing. Whereas a lack of activation function 1 (AF1) may underlie the reduced activity of the GR-D isoforms, it is not clear how the GR-C3 isoform has heightened activity. Mutation analyses and N-terminal tagging demonstrated that steric hindrance is probably the mechanism for the GR-A, -B, -C1, and -C2 isoforms to have lower activity than the GR-C3 isoform. In addition, truncation scanning analyses revealed that residues 98 to 115 are critical in the hyperactivity of the human GR-C3 isoform. Chimera constructs linking this critical fragment with the GAL4 DNA-binding domain showed that GR residues 98 to 115 do not contain any independent transactivation activity. Mutations at residues Asp101 or Gln106 and Gln107 all reduced the activity of the GR-C3 isoform. In addition, functional studies indicated that Asp101 is crucial for the GR-C3 isoform to recruit coregulators and to mediate glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Thus, charged and polar residues are essential components of an N-terminal motif that enhances the activity of AF1 and the GR-C3 isoform. These studies, together with the observations that GR isoforms have cell-specific expression patterns, provide a molecular basis for the tissue-specific functions of GR translational isoforms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Selective glucocorticoid receptor translational isoforms reveal glucocorticoid-induced apoptotic transcriptomes.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Jan 10;4(1):e453. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.193. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23303127 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor alpha isoform-selective regulation of antiapoptotic genes in osteosarcoma cells: a new mechanism for glucocorticoid resistance.Mol Endocrinol. 2011 Jul;25(7):1087-99. doi: 10.1210/me.2010-0051. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21527497 Free PMC article.
-
Translational regulatory mechanisms generate N-terminal glucocorticoid receptor isoforms with unique transcriptional target genes.Mol Cell. 2005 Apr 29;18(3):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.03.025. Mol Cell. 2005. PMID: 15866175
-
Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms generate transcription specificity.Trends Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;16(6):301-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2006.04.005. Epub 2006 May 11. Trends Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16697199 Review.
-
The origin and functions of multiple human glucocorticoid receptor isoforms.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Jun;1024:102-23. doi: 10.1196/annals.1321.008. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15265776 Review.
Cited by
-
A gradient of glucocorticoid sensitivity among helper T cell cytokines.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016 Oct;31:27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.05.002. Epub 2016 May 13. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016. PMID: 27235091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the molecular mechanisms determining tissue sensitivity to glucocorticoids: novel mutations, circadian rhythm and ligand-induced repression of the human glucocorticoid receptor.BMC Endocr Disord. 2014 Aug 25;14:71. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-14-71. BMC Endocr Disord. 2014. PMID: 25155432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BCL-2 protects human and mouse Th17 cells from glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis.Allergy. 2016 May;71(5):640-50. doi: 10.1111/all.12840. Epub 2016 Feb 4. Allergy. 2016. PMID: 26752231 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically tunable frustration controls allostery in an intrinsically disordered transcription factor.Elife. 2017 Oct 12;6:e30688. doi: 10.7554/eLife.30688. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29022880 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids improve sperm performance in physiological and pathological conditions: their role in sperm fight/flight response.Anat Cell Biol. 2024 Mar 31;57(1):119-128. doi: 10.5115/acb.23.164. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Anat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38098241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rhen T, Cidlowski JA. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids—new mechanisms for old drugs. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1711–1723 - PubMed
-
- Lu NZ, Cidlowski JA. Glucocorticoid receptor isoforms generate transcription specificity. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:301–307 - PubMed
-
- Oakley RH, Sar M, Cidlowski JA. The human glucocorticoid receptor β isoform. Expression, biochemical properties, and putative function. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:9550–9559 - PubMed
-
- Oakley RH, Webster JC, Sar M, Parker CR, Jr, Cidlowski JA. Expression and subcellular distribution of the β-isoform of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology. 1997;138:5028–5038 - PubMed
-
- Lu NZ, Cidlowski JA. Translational regulatory mechanisms generate N-terminal glucocorticoid receptor isoforms with unique transcriptional target genes. Mol Cell. 2005;18:331–342 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

