The miR-310/13 cluster antagonizes β-catenin function in the regulation of germ and somatic cell differentiation in the Drosophila testis
- PMID: 23821034
- PMCID: PMC3699279
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.092817
The miR-310/13 cluster antagonizes β-catenin function in the regulation of germ and somatic cell differentiation in the Drosophila testis
Abstract
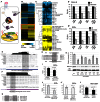
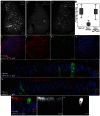
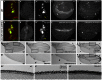
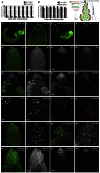
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are regulators of global gene expression and function in a broad range of biological processes. Recent studies have suggested that miRNAs can function as tumor suppressors or oncogenes by modulating the activities of evolutionarily conserved signaling pathways that are commonly dysregulated in cancer. We report the identification of the miR-310 to miR-313 (miR-310/13) cluster as a novel antagonist of Wingless (Drosophila Wnt) pathway activity in a functional screen for Drosophila miRNAs. We demonstrate that miR-310/13 can modulate Armadillo (Arm; Drosophila β-catenin) expression and activity by directly targeting the 3'-UTRs of arm and pangolin (Drosophila TCF) in vivo. Notably, the miR-310/13-deficient flies exhibit abnormal germ and somatic cell differentiation in the male gonad, which can be rescued by reducing Arm protein levels or activity. Our results implicate a previously unrecognized function for miR-310/13 in dampening the activity of Arm in early somatic and germline progenitor cells, whereby inappropriate/sustained activation of Arm-mediated signaling or cell adhesion may impact normal differentiation in the Drosophila male gonad.
Keywords: Armadillo; Beta-catenin; MicroRNA; Stem cells; Wingless.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probing the canonicity of the Wnt/Wingless signaling pathway.PLoS Genet. 2017 Apr 3;13(4):e1006700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006700. eCollection 2017 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28369070 Free PMC article.
-
Homeodomain-interacting protein kinases (Hipks) promote Wnt/Wg signaling through stabilization of beta-catenin/Arm and stimulation of target gene expression.Development. 2009 Jan;136(2):241-51. doi: 10.1242/dev.025460. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Development. 2009. PMID: 19088090
-
Coop functions as a corepressor of Pangolin and antagonizes Wingless signaling.Genes Dev. 2010 May;24(9):881-6. doi: 10.1101/gad.561310. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20439429 Free PMC article.
-
The Yin-Yang of TCF/beta-catenin signaling.Adv Cancer Res. 2000;77:1-24. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60783-6. Adv Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10549354 Review.
-
Modulating and measuring Wingless signalling.Methods. 2014 Jun 15;68(1):194-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2014.03.015. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Methods. 2014. PMID: 24675402 Review.
Cited by
-
Redundant and incoherent regulations of multiple phenotypes suggest microRNAs' role in stability control.Genome Res. 2017 Oct;27(10):1665-1673. doi: 10.1101/gr.222505.117. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Genome Res. 2017. PMID: 28904014 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of drosophila germline stem cell maintenance and differentiation.Dev Biol. 2021 May;473:105-118. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.02.003. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33610541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wingless/Wnt Signaling in Intestinal Development, Homeostasis, Regeneration and Tumorigenesis: A Drosophila Perspective.J Dev Biol. 2018 Mar 28;6(2):8. doi: 10.3390/jdb6020008. J Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29615557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA regulation of Wnt signaling pathways in development and disease.Cell Signal. 2015 Jul;27(7):1380-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Apr 2. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25843779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Rapid Evolving microRNA Cluster Rewires Its Target Regulatory Networks in Drosophila.Front Genet. 2021 Oct 28;12:760530. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.760530. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34777478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basler K., Struhl G. (1994). Compartment boundaries and the control of Drosophila limb pattern by hedgehog protein. Nature 368, 208–214 - PubMed
-
- Bushati N., Cohen S. M. (2007). microRNA functions. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 23, 175–205 - PubMed
-
- Calin G. A., Croce C. M. (2006). MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 857–866 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

