Smoking behaviours and cessation services among male physicians in China: evidence from a structural equation model
- PMID: 23821489
- PMCID: PMC3756466
- DOI: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2012-050884
Smoking behaviours and cessation services among male physicians in China: evidence from a structural equation model
Abstract
Objective: To investigate smoking prevalence and cessation services provided by male physicians in hospitals in three Chinese cities.
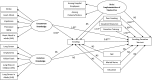
Methods: Data were collected from a survey of male physicians employed at 33 hospitals in Changsha, Qingdao and Wuxi City (n=720). Exploratory factor analysis was performed to identify latent variables, and confirmatory structural equation modelling analysis was performed to test the relationships between predictor variables and smoking in male physicians, and their provision of cessation services.
Results: Of the sampled male physicians, 25.7% were current smokers, and 54.0% provided cessation services by counselling (18.8%), distributing self-help materials (17.1%), and providing traditional remedies or medication (18.2%). Factors that predicted smoking included peer smoking (OR 1.14 95% CI 1.03 to 1.26) and uncommon knowledge (OR 0.94 95% CI 0.89 to 0.99), a variable measuring awareness of the association of smoking with stroke, heart attack, premature ageing and impotence in male adults as well as the role of passive smoking in heart attack. Factors that predicted whether physicians provided smoking cessation services included peer smoking (OR 0.82 95% CI 0.76 to 0.89), physicians' own smoking (OR 0.87 95% CI 0.81 to 0.93), training in cessation (OR 1.36 95% CI 1.27 to 1.45) and access to smoking cessation resources (OR 1.69 95% CI 1.58 to 1.82).
Conclusions: The smoke-free policy is not strictly implemented at healthcare facilities, and smoking remains a public health problem among male physicians. A holistic approach, including a stricter implementation of the smoke-free policy, comprehensive education on the hazards of smoking, training in standard smoking-cessation techniques and provision of cessation resources, is needed to curb the smoking epidemic among male physicians and to promote smoking cessation services in China.
Keywords: Cessation; Global health; Health Services; Public policy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of physicians' smoking status on their knowledge, attitude, opinions and practices of smoking cessation in a University Hospital, in Egypt.J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2017 Jun 1;92(2):96-106. doi: 10.21608/epx.2018.8947. J Egypt Public Health Assoc. 2017. PMID: 30184407
-
Awareness, practices, and barriers regarding smoking cessation treatment among physicians in Saudi Arabia.J Addict Dis. 2017 Jan-Mar;36(1):53-59. doi: 10.1080/10550887.2015.1116355. Epub 2015 Nov 13. J Addict Dis. 2017. PMID: 26566876
-
Knowledge of female doctors about smoking risks and their attitude toward cessation in antenatal clinics - perspective from tertiary care hospitals in Karachi.J Pak Med Assoc. 2017 Dec;67(12):1809-1813. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017. PMID: 29256521
-
A review of smoke-free health care in mainland China.Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011 Apr;15(4):453-8. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.10.0049. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2011. PMID: 21396202 Review.
-
Health care providers' engagement in smoking cessation with pregnant smokers.J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2010 Jan-Feb;39(1):64-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6909.2009.01084.x. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2010. PMID: 20409104 Review.
Cited by
-
The global tobacco control 'endgame': change the policy environment to implement the FCTC.J Public Health Policy. 2014 Nov;35(4):506-17. doi: 10.1057/jphp.2014.18. Epub 2014 May 15. J Public Health Policy. 2014. PMID: 24831675
-
A Scoping Review of Maternal and Child Health Clinicians Attitudes, Beliefs, Practice, Training and Perceived Self-Competence in Environmental Health.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015 Dec 10;12(12):15769-81. doi: 10.3390/ijerph121215018. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2015. PMID: 26690461 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of long-term abstinence in a randomized controlled trial of smoking cessation by mobile phone text messaging ('Happy Quit') in China.Tob Prev Cessat. 2022 Aug 5;8:31. doi: 10.18332/tpc/152255. eCollection 2022. Tob Prev Cessat. 2022. PMID: 35991840 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of education methods on self-efficacy of smoking cessation counseling among medical students.PeerJ. 2021 May 7;9:e11408. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11408. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34012731 Free PMC article.
-
Are physicians aware of their role in tobacco control? A conference-based survey in Portugal.BMC Public Health. 2014 Sep 20;14:979. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-979. BMC Public Health. 2014. PMID: 25239241 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Q, Hsia J, Yang G. Prevalence of smoking in China in 2010. N Engl J Med 2011;364:2469–70 - PubMed
-
- Abdullah AS, Qiming F, Pun V, et al. A review of tobacco smoking and smoking cessation practices among physicians in China: 1987–2010. Tob Control 2013;22:9–14 - PubMed
-
- Yan J, Xiao S, Ouyang D, et al. Smoking behavior, knowledge, attitudes and practice among health care providers in Changsha city, China. Nicotine Tob Res 2008;10:737–44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
