Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: the Achilles' heel of lung transplantation
- PMID: 23821508
- PMCID: PMC4768744
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0033-1348467
Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome: the Achilles' heel of lung transplantation
Abstract
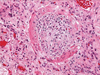
Lung transplantation is a therapeutic option for patients with end-stage pulmonary disorders. Unfortunately, chronic lung allograft dysfunction (CLAD), most commonly manifest as bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS), continues to be highly prevalent and is the major limitation to long-term survival. The pathogenesis of BOS is complex and involves alloimmune and nonalloimmune pathways. Clinically, BOS manifests as airway obstruction and dyspnea that are classically progressive and ultimately fatal; however, the course is highly variable, and distinguishable phenotypes may exist. There are few controlled studies assessing treatment efficacy, but only a minority of patients respond to current treatment modalities. Ultimately, preventive strategies may prove more effective at prolonging survival after lung transplantation, but their remains considerable debate and little data regarding the best strategies to prevent BOS. A better understanding of the risk factors and their relationship to the pathological mechanisms of chronic lung allograft rejection should lead to better pharmacological targets to prevent or treat this syndrome.
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Figures




References
-
- Christie JD, Edwards LB, Kucheryavaya AY, et al. International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: 29th adult lung and heart-lung transplant report-2012. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2012;31(10):1073–1086. - PubMed
-
- Knoop C, Estenne M. Acute and chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2006;27(5):521–533. - PubMed
-
- Vermeulen KM, Groen H, van der Bij W, Erasmus ME, Koëter GH, TenVergert EM. The effect of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome on health related quality of life. Clin Transplant. 2004;18(4):377–383. - PubMed
-
- van den Berg JW, van Enckevort PJ, TenVergert EM, Postma DS, van der Bij W, Koëter GH. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome and additional costs of lung transplantation. Chest. 2000;118(6):1648–1652. - PubMed
-
- Estenne M, Maurer JR, Boehler A, et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome 2001: an update of the diagnostic criteria. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2002;21(3):297–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

