The acute swollen knee: diagnosis and management
- PMID: 23821708
- PMCID: PMC3704066
- DOI: 10.1177/0141076813482831
The acute swollen knee: diagnosis and management
Abstract
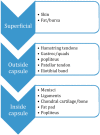
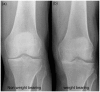
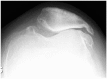
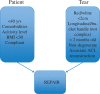
The acutely swollen knee is a common presentation of knee pathology in both primary care and the emergency department. The key to diagnosis and management is a thorough history and examination to determine the primary pathology, which includes inflammation, infection or a structural abnormality in the knee. The location of pain and tenderness can aid to localization of structural pathology even before radiological tests are requested, and indeed inform the investigations that should be carried out. Aspiration of an acutely swollen knee can aid diagnosis and help relieve pain. The management of the swollen knee depends on underlying pathology and can range from anti-inflammatory medication for inflammation to operative intervention for a structural abnormality.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The acutely swollen knee. Part two--management of traumatic pathology.J R Nav Med Serv. 2014;100(2):186-92. J R Nav Med Serv. 2014. PMID: 25335315 Review.
-
The acutely swollen knee. Part 1: Management of atraumatic pathology.J R Nav Med Serv. 2014;100(1):24-33. J R Nav Med Serv. 2014. PMID: 24881423
-
Knee Pain in Children, Part III: Stress Injuries, Benign Bone Tumors, Growing Pains.Pediatr Rev. 2016 Mar;37(3):114-8; quiz 119. doi: 10.1542/pir.2015-0042. Pediatr Rev. 2016. PMID: 26933226 Review. No abstract available.
-
The location of knee pain and pathology in patients with a presumed meniscus tear: preoperative symptoms compared to arthroscopic findings.Ir J Med Sci. 2014 Mar;183(1):23-31. doi: 10.1007/s11845-013-0965-3. Epub 2013 May 12. Ir J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 23666820
-
[The painful knee in children].Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2024 Aug;53(8):553-556. doi: 10.1007/s00132-024-04535-1. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2024. PMID: 39039247 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Native Joint Septic Arthritis.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;13(7):596. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070596. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid/diminazene aceturate combination ameliorates osteoarthritic anomalies in a rodent model: a role of the ACE2/Ang1-7/MasR axis.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Dec;31(6):3263-3279. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01335-5. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37725260 Free PMC article.
-
Generalised knee swelling in adults.Singapore Med J. 2022 Apr;63(4):187-191. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2022054. Singapore Med J. 2022. PMID: 35698425 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Assessing diagnostic challenges in acute soft-tissue knee injuries.Bone Jt Open. 2024 Nov 6;5(11):984-991. doi: 10.1302/2633-1462.511.BJO-2024-0159.R1. Bone Jt Open. 2024. PMID: 39500364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kruseman N, Geesink RGT, van der Linden AJ et al. Acute knee injuries: diagnostic & treatment management proposals. See http://arnos.unimasas.nl/show.cgi?fig1?46875 (last checked 5 April 2013)
-
- Powers CM, Lilley JC, Lee TQ. The effects of axial and multi-plane loading of the extensor mechanism on the patellofemoral joint. Clin Biomech 1998; 13: 616–24 - PubMed
-
- Csintalan RP, Schulz MM, Woo J, McMahon PJ, Lee TQ. Gender differences in patellofemoral joint biomechanics. Clinical Orthopaed Related Res 2002; 402: 260–9 - PubMed
-
- Woolhead G, Gooberman-Hill R, Dieppe P, Hawker G. Night pain in hip and knee osteoarthritis: a focus group study. Arthritis Care Res 2010; 62: 944–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

