Iron and citrate export by a major facilitator superfamily pump regulates metabolism and stress resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium
- PMID: 23821749
- PMCID: PMC3718157
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1218274110
Iron and citrate export by a major facilitator superfamily pump regulates metabolism and stress resistance in Salmonella Typhimurium
Abstract
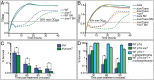
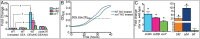
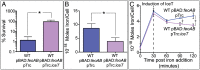
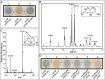
The efficacy of antibiotics and host defenses has been linked to the metabolic and redox states of bacteria. In this study we report that a stress-induced export pump belonging to the major facilitator superfamily effluxes citrate and iron from the enteric pathogen Salmonella Typhimurium to arrest growth and ameliorate the effects of antibiotics, hydrogen peroxide, and nitric oxide. The transporter, formerly known as MdtD, is now designated IceT (iron citrate efflux transporter). Iron efflux via an iron-chelating tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediate provides a direct link between aerobic metabolism and bacterial stress responses, representing a unique mechanism of resistance to host defenses and antimicrobial agents of diverse classes.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MntP and YiiP Contribute to Manganese Efflux in Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium under Conditions of Manganese Overload and Nitrosative Stress.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0131621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01316-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35019706 Free PMC article.
-
Linearized Siderophore Products Secreted via MacAB Efflux Pump Protect Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium from Oxidative Stress.mBio. 2020 May 5;11(3):e00528-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00528-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32371597 Free PMC article.
-
A Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) Efflux Pump, SCO4121, from Streptomyces coelicolor with Roles in Multidrug Resistance and Oxidative Stress Tolerance and Its Regulation by a MarR Regulator.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021 Mar 11;87(7):e02238-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02238-20. Print 2021 Mar 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33483304 Free PMC article.
-
S. Typhimurium strategies to resist killing by cationic antimicrobial peptides.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Nov;1848(11 Pt B):3021-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.01.013. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25644871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporters.J Membr Biol. 2017 Dec;250(6):573-585. doi: 10.1007/s00232-017-9982-x. Epub 2017 Aug 29. J Membr Biol. 2017. PMID: 28852815 Review.
Cited by
-
The Two-Component System CpxRA Affects Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Formation in Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli.Animals (Basel). 2023 Jan 23;13(3):383. doi: 10.3390/ani13030383. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766272 Free PMC article.
-
The Origins of ST11 KL64 Klebsiella pneumoniae: a Genome-Based Study.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Mar 27;11(2):e0416522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04165-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36971550 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Facilitates Iron Acquisition through UMPylation of Ferric Uptake Regulator.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0020722. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00207-22. Epub 2022 May 9. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35532216 Free PMC article.
-
The ins and outs of bacterial iron metabolism.Mol Microbiol. 2014 Aug;93(4):609-16. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12709. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Mol Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25040830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella-how a metabolic generalist adopts an intracellular lifestyle during infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015 Jan 29;4:191. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00191. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25688337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Hayete B, Lawrence CA, Collins JJ. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell. 2007;130(5):797–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

