MicroRNA in Alzheimer's disease: an exploratory study in brain, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma
- PMID: 23822153
- PMCID: PMC3967870
- DOI: 10.3109/1354750X.2013.814073
MicroRNA in Alzheimer's disease: an exploratory study in brain, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma
Abstract
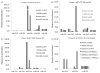
MicroRNA (miRNA) may be potential biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The objective of this investigation was to demonstrate that miRNAs in human brain or biofluids are differentially expressed according to disease status, tissue type, neuritic plaque score or Braak stage. Post-mortem brain (PMB) miRNA were profiled using arrays and validated using quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). Five qRT-PCR-validated miRNAs were measured in an independent sample of PMB, cerebrospinal fluid and plasma from the same subjects. Plasma miR-15a was found to be associated with plaque score in the independent sample. In conclusion, miRNA present in human biofluids may offer utility as biomarkers of AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

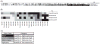
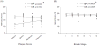

References
-
- Consensus recommendations for the postmortem diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The National Institute on Aging, and Reagan Institute Working Group on Diagnostic Criteria for the Neuropathological Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:S1–2. - PubMed
-
- Aqeilan RI, Calin GA, Croce CM. miR-15a and miR-16-1 in cancer: discovery, function and future perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17:215–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
