Trends of childhood obesity in China and associated factors
- PMID: 23823460
- PMCID: PMC4247345
- DOI: 10.1177/1054773813493286
Trends of childhood obesity in China and associated factors
Abstract
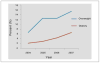
Childhood obesity is worsening at dramatic rates and has become a public health crisis. This study investigated these trends in childhood obesity and examined parental factors that may contribute to overweight and obesity. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated from height and weight measurements taken annually from 2004 to 2007 in a subsample of 136 children (2-4 years old), from the Jintan Child Health Project in China. Parental factors were assessed through a self-administered questionnaire. Prevalence rates of overweight and obesity rose from 6.6% and 2.2% in 2004 to 15.4% and 6.6% in 2007 (p < .05). Overweight was significantly associated with maternal employment (p < .05), but not with parental education level, maternal age at birth, or breast-feeding. To counter this rapid increase of obesity and overweight prevalence, nurses should regularly monitor children's weight and advise parents, especially working mothers, on the nutritional benefits of home-cooked meals.
Keywords: maternal employment; obesity; overweight; preschool children.
© The Author(s) 2013.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Aeberli I, Kaspar M, Zimmermann MB. Dietary intake and physical activity of normal weight and overweight 6-to 14-year-old Swiss children. Swiss Medical Weekly. 2007;137:424–430. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PM. Parental employment, family routines and childhood obesity. Economics & Human Biology. 2012;10:340–351. - PubMed
-
- Anderson PM, Butcher KF, Levine PB. Maternal employment and overweight children. Journal of Health Economics. 2003;22:477–504. - PubMed
-
- Arenz S, Ruckerl R, Koletzko B, von Kries R. Breast-feeding and childhood obesity—A systematic review. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 2004;28:1247–1256. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical