Chronic AT2 receptor activation increases renal ACE2 activity, attenuates AT1 receptor function and blood pressure in obese Zucker rats
- PMID: 23823602
- PMCID: PMC4091804
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2013.193
Chronic AT2 receptor activation increases renal ACE2 activity, attenuates AT1 receptor function and blood pressure in obese Zucker rats
Abstract
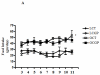
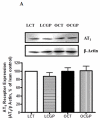
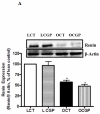
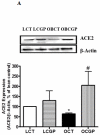
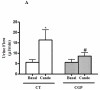
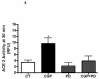
Abnormal regulation of the renin angiotensin system such as enhanced renal AT1R function and reduced ACE2 activity contributes to obesity-related hypertension. Here, we tested whether long-term AT2R activation affects renal function in obesity using lean and obese Zucker rats treated with the AT2R agonist CGP42112A for 2 weeks. This caused blood pressure to decrease by 13 mm Hg, which was associated with increased urinary sodium excretion in the obese rats. Cortical ACE2 expression and activity, the Mas receptor (MasR), and its ligand angiotensin-(1-7) were all increased in CGP-treated obese compared with control rats. Candesartan-induced natriuresis, a measure of AT₁R function, was reduced but cortical AT₁R expression and angiotensin II levels were similar in CGP-treated obese compared with control rats. Renin and AT2R expression in obese rats was not affected by CGP treatment. In HK-2 cells in vitro, CGP treatment caused increased ACE2 activity and MasR levels but decreased AT₁R levels and renin activity. Thus, long-term AT2R activation shifts the opposing arms of renin angiotensin system and contributes to natriuresis and blood pressure reduction in obese animals. Our study highlights the importance of AT2R as a target for treating obesity-related hypertension.
Figures

















References
-
- Vickers C, Hales P, Kaushik V, et al. Hydrolysis of biological peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:14838–14843. - PubMed
-
- de Gasparo M, Catt KJ, Inagami T, et al. International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:415–472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

