Crystal Structure of Crataeva tapia Bark Protein (CrataBL) and Its Effect in Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines
- PMID: 23823708
- PMCID: PMC3688800
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064426
Crystal Structure of Crataeva tapia Bark Protein (CrataBL) and Its Effect in Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
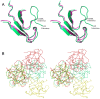
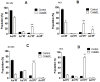
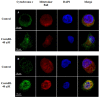
A protein isolated from the bark of Crataeva tapia (CrataBL) is both a Kunitz-type plant protease inhibitor and a lectin. We have determined the amino acid sequence and three-dimensional structure of CrataBL, as well as characterized its selected biochemical and biological properties. We found two different isoforms of CrataBL isolated from the original source, differing in positions 31 (Pro/Leu); 92 (Ser/Leu); 93 (Ile/Thr); 95 (Arg/Gly) and 97 (Leu/Ser). CrataBL showed relatively weak inhibitory activity against trypsin (Kiapp = 43 µM) and was more potent against Factor Xa (Kiapp = 8.6 µM), but was not active against a number of other proteases. We have confirmed that CrataBL contains two glycosylation sites and forms a dimer at high concentration. The high-resolution crystal structures of two different crystal forms of isoform II verified the β-trefoil fold of CrataBL and have shown the presence of dimers consisting of two almost identical molecules making extensive contacts (∼645 Å(2)). The structure differs from those of the most closely related proteins by the lack of the N-terminal β-hairpin. In experiments aimed at investigating the biological properties of CrataBL, we have shown that addition of 40 µM of the protein for 48 h caused maximum growth inhibition in MTT assay (47% of DU145 cells and 43% of PC3 cells). The apoptosis of DU145 and PC3 cell lines was confirmed by flow cytometry using Annexin V/FITC and propidium iodide staining. Treatment with CrataBL resulted in the release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and in the activation of caspase-3 in DU145 and PC3 cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures









Similar articles
-
Potential of the Lectin/Inhibitor Isolated from Crataeva tapia Bark (CrataBL) for Controlling Callosobruchus maculatus Larva Development.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Dec 9;63(48):10431-6. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03634. Epub 2015 Dec 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26568149 Free PMC article.
-
A Bifunctional Molecule with Lectin and Protease Inhibitor Activities Isolated from Crataeva tapia Bark Significantly Affects Cocultures of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Glioblastoma Cells.Molecules. 2019 Jun 4;24(11):2109. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112109. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31167364 Free PMC article.
-
Crataeva tapia bark lectin is an affinity adsorbent and insecticidal agent.Plant Sci. 2012 Feb;183:20-6. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.10.018. Epub 2011 Nov 4. Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22195573
-
CrataBL, a lectin and Factor Xa inhibitor, plays a role in blood coagulation and impairs thrombus formation.Biol Chem. 2014 Sep;395(9):1027-35. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2014-0127. Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25153385
-
Crataeva tapia bark lectin (CrataBL) is a chemoattractant for endothelial cells that targets heparan sulfate and promotes in vitro angiogenesis.Biochimie. 2019 Nov;166:173-183. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.04.011. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Biochimie. 2019. PMID: 30981871
Cited by
-
Potential of the Lectin/Inhibitor Isolated from Crataeva tapia Bark (CrataBL) for Controlling Callosobruchus maculatus Larva Development.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Dec 9;63(48):10431-6. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03634. Epub 2015 Dec 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 26568149 Free PMC article.
-
Could a plant derived protein potentiate the anticancer effects of a stem cell in brain cancer?Oncotarget. 2018 Apr 20;9(30):21296-21312. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25090. eCollection 2018 Apr 20. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29765540 Free PMC article.
-
Canonical or noncanonical? Structural plasticity of serine protease-binding loops in Kunitz-STI protease inhibitors.Protein Sci. 2023 Feb;32(2):e4570. doi: 10.1002/pro.4570. Protein Sci. 2023. PMID: 36660780 Free PMC article.
-
Binding kinetics of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles with proteins.Nanoscale. 2018 Feb 15;10(7):3235-3244. doi: 10.1039/c7nr06810g. Nanoscale. 2018. PMID: 29383361 Free PMC article.
-
A Bifunctional Molecule with Lectin and Protease Inhibitor Activities Isolated from Crataeva tapia Bark Significantly Affects Cocultures of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Glioblastoma Cells.Molecules. 2019 Jun 4;24(11):2109. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112109. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31167364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murzin AG, Lesk AM, Chothia C (1992) Beta-Trefoil fold. Patterns of structure and sequence in the Kunitz inhibitors interleukins-1 beta and 1 alpha and fibroblast growth factors. J Mol Biol 223: 531–543. - PubMed
-
- Renko M, Sabotič J, Turk D (2012) Beta trefoil inhibitors from the work of Kunitz onwards. Biol Chem 393: 2043–1054. - PubMed
-
- Azarkan M, Dibiani R, Goormaghtigh E, Raussens V, Baeyens-Volant D (2006) The papaya Kunitz-type trypsin inhibitor is a highly stable beta-sheet glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764: 1063–1072. - PubMed
-
- Birk Y (2005) Plant protease inhibitors: significance in nutrition, plant protection, cancer prevention and genetic engineering. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
-
- Horigome D, Satoh H, Itoh N, Mitsunaga K, Oonishi I, et al. (2007) Structural mechanism and photoprotective function of water-soluble chlorophyll-binding protein. J Biol Chem 282: 6525–6531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

