TLR3, TLR4 and TLRs7-9 Induced Interferons Are Not Impaired in Airway and Blood Cells in Well Controlled Asthma
- PMID: 23824215
- PMCID: PMC3688823
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065921
TLR3, TLR4 and TLRs7-9 Induced Interferons Are Not Impaired in Airway and Blood Cells in Well Controlled Asthma
Abstract
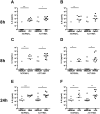
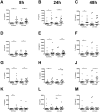
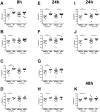
Defective Rhinovirus induced interferon-β and interferon-λ production has been reported in bronchial epithelial cells from asthmatics but the mechanisms of defective interferon induction in asthma are unknown. Virus infection can induce interferon through Toll like Receptors (TLR)3, TLR7 and TLR8. The role of these TLRs in interferon induction in asthma is unclear. This objective of this study was to measure the type I and III interferon response to TLR in bronchial epithelial cells and peripheral blood cells from atopic asthmatics and non-atopic non-asthmatics. Bronchial epithelial cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells from atopic asthmatic and non-atopic non-asthmatic subjects were stimulated with agonists to TLR3, TLR4 & TLRs7-9 and type I and III interferon and pro-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin(IL)-6 and IL-8, responses assessed. mRNA expression was analysed by qPCR. Interferon proteins were analysed by ELISA. Pro-inflammatory cytokines were induced by each TLR ligand in both cell types. Ligands to TLR3 and TLR7/8, but not other TLRs, induced interferon-β and interferon-λ in bronchial epithelial cells. The ligand to TLR7/8, but not those to other TLRs, induced only type I interferons in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. No difference was observed in TLR induced interferon or pro-inflammatory cytokine production between asthmatic and non-asthmatic subjects from either cell type. TLR3 and TLR7/8,, stimulation induced interferon in bronchial epithelial cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Interferon induction to TLR agonists was not observed to be different in asthmatics and non-asthmatics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rhinovirus 16-induced IFN-α and IFN-β are deficient in bronchoalveolar lavage cells in asthmatic patients.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Jun;129(6):1506-1514.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.03.044. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22657407
-
TLR3 and MDA5 signalling, although not expression, is impaired in asthmatic epithelial cells in response to rhinovirus infection.Clin Exp Allergy. 2014 Jan;44(1):91-101. doi: 10.1111/cea.12218. Clin Exp Allergy. 2014. PMID: 24131248
-
Raised interferon-β, type 3 interferon and interferon-stimulated genes - evidence of innate immune activation in neutrophilic asthma.Clin Exp Allergy. 2017 Mar;47(3):313-323. doi: 10.1111/cea.12809. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Clin Exp Allergy. 2017. PMID: 27622317
-
Regulation and Function of Interferon-Lambda (IFNλ) and Its Receptor in Asthma.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 10;12:731807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731807. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34899691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Toll-like receptor-dependent induction of interferons in protective immunity to viruses.Immunol Rev. 2007 Dec;220(1):225-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2007.00564.x. Immunol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17979850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Type I interferons and endoplasmic reticulum stress in health and disease.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020;350:63-118. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2019.10.004. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32138904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-triggered exacerbation in allergic asthmatic children: neutrophilic airway inflammation and alteration of virus sensors characterize a subgroup of patients.Respir Res. 2017 Nov 14;18(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12931-017-0672-0. Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 29137638 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Respiratory Viruses and Asthma.Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018 Feb;39(1):45-55. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1617412. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2018. PMID: 29427985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral and host factors determine innate immune responses in airway epithelial cells from children with wheeze and atopy.Thorax. 2014 Oct;69(10):918-25. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-204908. Epub 2014 May 7. Thorax. 2014. PMID: 24811725 Free PMC article.
-
TLR2 Regulates Allergic Airway Inflammation and Autophagy Through PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2017 Aug;40(4):1382-1392. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0581-x. Inflammation. 2017. PMID: 28493079
References
-
- Weiss KB, Sullivan SD (2001) The health economics of asthma and rhinitis. I. Assessing the economic impact. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107: 3–8. - PubMed
-
- Corne JM, Marshall C, Smith S, Schreiber J, Sanderson G, et al. (2002) Frequency, severity, and duration of rhinovirus infections in asthmatic and non-asthmatic individuals: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 359: 831–834. - PubMed
-
- Khaitov MR, Laza-Stanca V, Edwards MR, Walton RP, Rohde G, et al. (2009) Respiratory virus induction of alpha-, beta- and lambda-interferons in bronchial epithelial cells and peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Allergy 64: 375–386. - PubMed
-
- Contoli M, Message SD, Laza-Stanca V, Edwards MR, Wark PA, et al. (2006) Role of deficient type III interferon-lambda production in asthma exacerbations. Nat Med 12: 1023–1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

